FIG 2 .
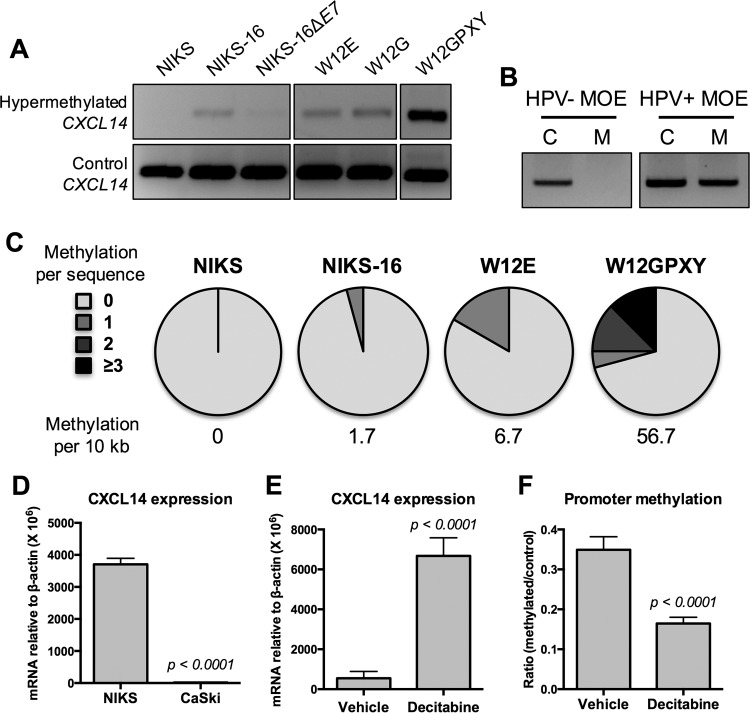
CXCL14 downregulation in HPV-positive epithelial cells is associated with CXCL14 promoter hypermethylation. (A and B) Genomic DNA was extracted from NIKS, NIKS-16, NIKS-16ΔE7, W12E, W12G, and W12GPXY cells (A) and MOE/shPTPN13 (HPV-negative) and MOE/E6E7 (HPV-positive) cells (B). MSP was performed using specific primers and analyzed in 1.2% agarose gel as described in Text S1 in the supplemental material. (B) MSP products of the control and hypermethylated Cxcl14 promoter are shown in lanes C and M, respectively. (C) Bisulfite PCR products were cloned into the pGEM-T Easy vector and sequenced. (D) CXCL14 expression was measured as described in the legend to Fig. 1. (E and F) CaSki cells were treated with 10 µM decitabine for 6 days or with a vehicle control (H2O) for 6 days. RT-qPCR (E) and qMSP (F) were performed using total RNA and genomic DNA, respectively. CXCL14 mRNA copy numbers were normalized by β-actin mRNA (D and E). (F) Changes in CXCL14 promoter methylation were calculated by using the 2−ΔΔCT method and shown as a fold ratio of methylated signal over total signal. P values were determined by Student’s t test.