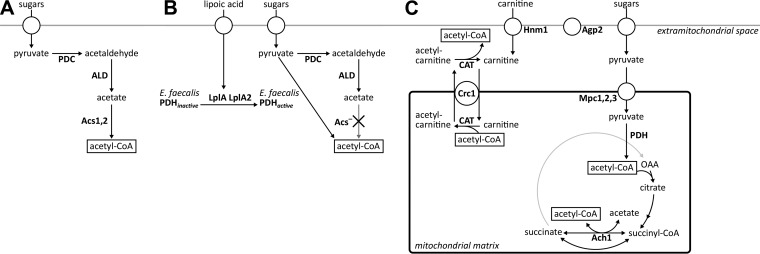
FIG 1 .
Cytosolic acetyl-CoA metabolism in (engineered) Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. (A) In wild-type strains, cytosolic acetyl-CoA is produced via the PDH bypass, consisting of pyruvate carboxylase, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, and acetyl-CoA synthetase. (B) Replacing the native route of acetyl-CoA synthesis by the Enterococcus faecalis PDH complex requires the extracellular addition of lipoic acid for activation of the E2 subunit of the cytosolically expressed bacterial PDH complex. (C) In the evolved strains IMS0482 and IMS0483, extracellular l-carnitine is imported into the mitochondria via the Hnm1 transporter at the plasma membrane and the Crc1 transporter at the inner mitochondrial membrane. Pyruvate is imported into the mitochondria, following its oxidative decarboxylation by the native mitochondrial PDH complex. The acetyl moiety is then transferred to l-carnitine, followed by export of acetyl-l-carnitine to the cytosol. There, carnitine acetyltransferases move the acetyl moiety back to CoA, yielding cytosolic acetyl-CoA. Abbreviations: Ach1, CoA transferase; Acs, Acs1, and Acs2, acetyl-CoA synthetase; Agp2, regulator; ALD, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase; CAT, carnitine acetyltransferase; Crc1, acetyl-carnitine translocase; Hnm1, carnitine transporter; LplA and LplA2, lipoylation proteins; Mpc1, Mpc2, and Mpc3, mitochondrial pyruvate carrier; OAA, oxaloacetate; PDC, pyruvate decarboxylase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.