Figure 1.
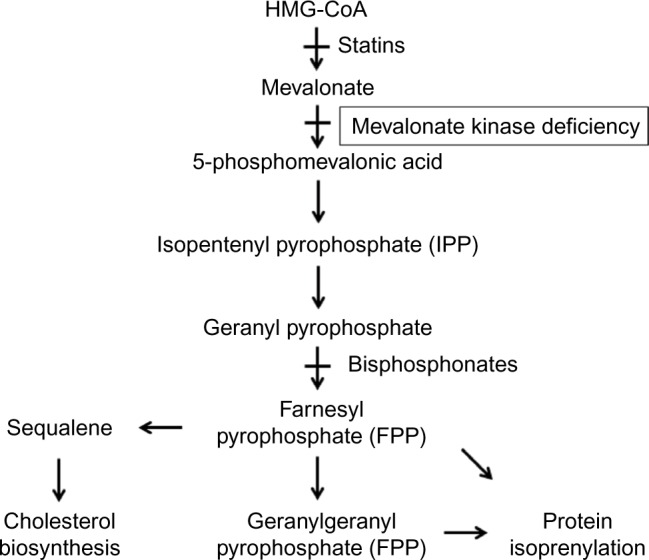
Overview of the mevalonate pathway.
Notes: The pathway starts with conversation of HMG-CoA into mevalonate through the action of HMG-CoA reductase. Mevalonate is then converted into 5-phosphomevalonic acid by mevalonate kinase. In MKD, there is inhibition of the pathway at this step, leading to buildup of mevalonic acid and depletion of downstream products. 5-Phosphomevalonic acid is ultimately converted to geranyl pyrophosphate, which serves as precursor for the isoprenoids farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP), which are the substrates for protein prenylation. This pathway can also be experimentally inhibited using statins, which block HMG-CoA reductase, or bisphosphonates, which block farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase.
Abbreviations: HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A; MKD, mevalonate kinase deficiency.
