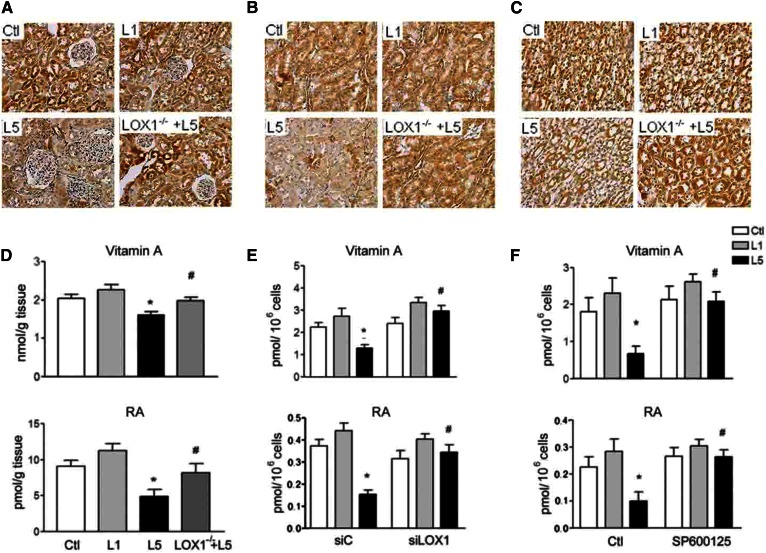
Fig. 6.
L5 decreases vitamin A and RA in kidneys and renal cells. Representative images show immunohistochemical staining for vitamin A in sections of cortex (A), outer medulla (B), and inner medulla (C) from saline-injected (Ctl), L1-injected (L1), L5-injected (L5), and L5-injected LOX1−/− mice (LOX1−/−+L5). D: Vitamin A and RA concentration decreased in the kidneys of L5-injected mice as compared with Ctl, L1, and L5 LOX1−/− mice (n = 3). Error bars of all experiments indicate mean ± SE. *P < 0.05 versus Ctl and L1; #P < 0.05 versus L5. E: ELISA assay showed that LOX1 siRNA transfection reversed the reduction of vitamin A and RA level under L5 stimulation in HK-2 cells (n = 3). Error bars of all experiments indicate mean ± SE. *P < 0.05 versus Ctl and L1-treated siC cells; #P < 0.05 versus L5-treated siC cells. F: ELISA revealed that SP600125 treatment reversed the reduction of vitamin A and RA level under L5 stimulation in cell lysate of RETCs (n = 3). All results are represented as mean ± SE. *P < 0.05 versus Ctl and L1; #P < 0.05 versus L5.