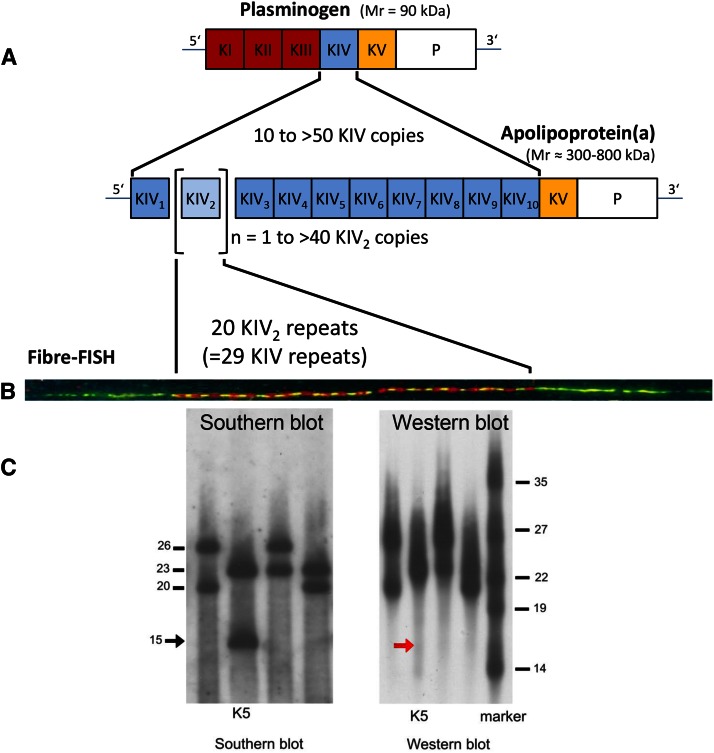
Fig. 1.
A: Schematic illustration of the structural homology between PLG and apo(a). PLG contains five different kringle structures (KI–KV) and a PD. The apo(a) is missing KI to KIII, but has a variable number of KIV copies. The minimum number is 10 (KIV-1 to KIV-10, including one copy of KIV-2). An individual can have more than 40 KIV-2 copies, which is the variable part of apo(a). Adapted and reprinted with permission of (2). B: Illustration of a two-color fiber-FISH image of the LPA KIV-2 domain from a 20-repeat allele using 4 kb (red) and 1.2 kb (green) intron probes, which enable the KIV-2 repeat number to be counted [for details see (139)]. C: Analysis of four samples from one family by PFGE/Southern blotting and Western blotting. This analysis demonstrates a null allele by simultaneous analysis of DNA by PFGE/Southern blotting (left) and plasma by Western blotting (right) from the same individuals. The arrow marks the absence of a signal corresponding to the allele with 15 KIV-2 repeats on the Western blot of the individual marked as K5. Figure adapted and reprinted with permission from (200).