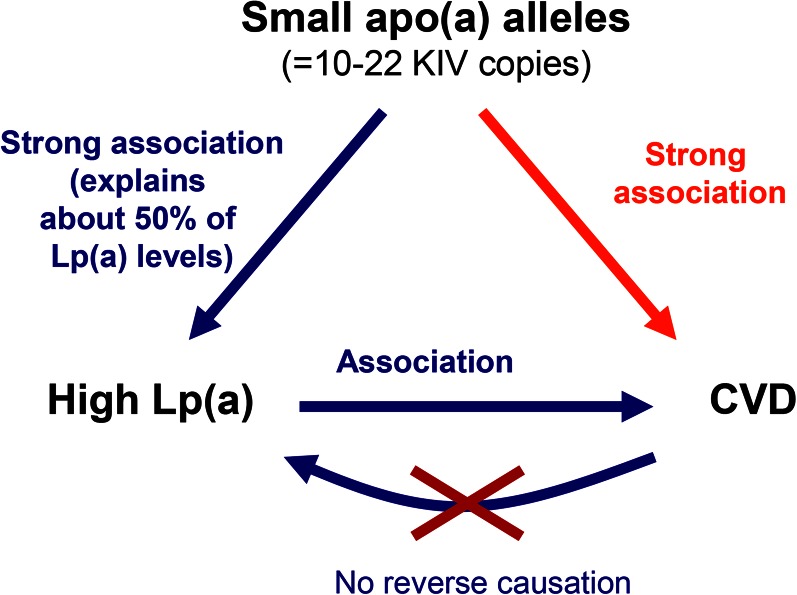
Fig. 7.
Mendelian randomization approach to demonstrate a causal association between Lp(a) concentration and CHD. Because a low number of KIV copies (11–22 copies) is associated with high Lp(a) levels and high Lp(a) levels are associated with CHD, it follows that a low number of KIV copies will be associated with CHD if the association between Lp(a) and CHD is causal. As the latter is indeed the case, reverse causation [i.e., that CHD is secondarily causing an increase in Lp(a) levels] can be excluded. Figure reprinted with permission of (2).