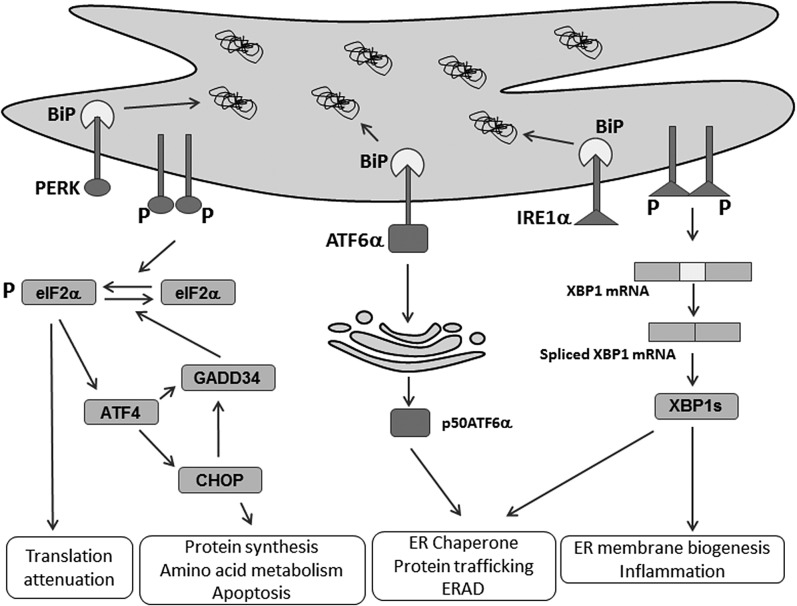
Fig. 1.
ER stress and the UPR. Numerous environmental, physiological, and pathological insults cause ER stress and activate the UPR. The UPR is signaled by three ER membrane-bound proteins, PERK, IRE1α, and ATF6α, to resolve ER homeostasis through translational and transcriptional changes in response to ER stress. PERK phosphorylates eIF2α to attenuate protein synthesis, which preferentially activates ATF4 mRNA translation to induce its target genes, CHOP and GADD34. Activated IRE1α cleaves XBP1 mRNA to produce a spliced form that translates a novel polypeptide, XBP1s, to upregulate genes involved in ER membrane biogenesis, ER folding and trafficking, and ERAD. ATF6α traffics to Golgi apparatus for cleavage by S1P and S2P, which release p50ATF6α that transcriptionally induces its target genes encoding ER chaperone and ERAD functions.