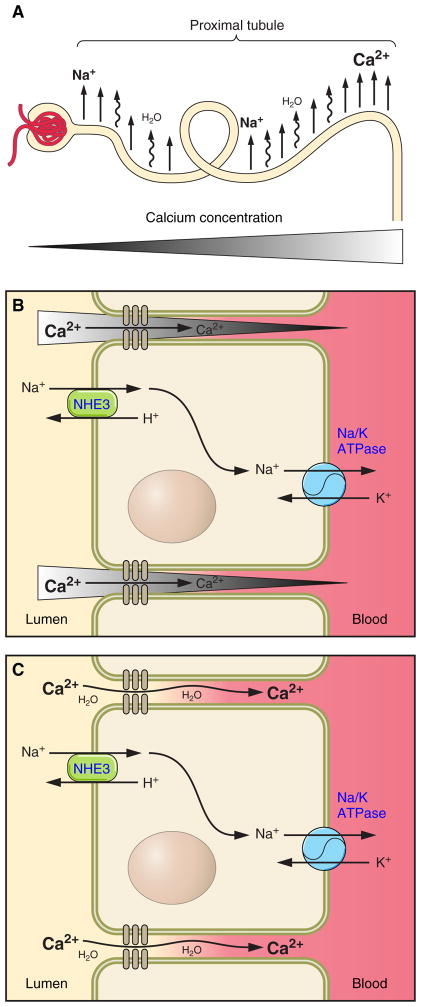
Fig. 1.
Diagrammatic representation of proximal tubular Ca2+ reabsorption. Filtered Na+ is reabsorbed from the proximal tubule (A), creating the osmotic driving force for water reabsorption, which, in turn, drives paracellular Ca2+ reabsorption either by creating a concentration gradient for Ca2+ (water removal increases the luminal concentration of Ca2+; B) or by convection/solvent drag (C). NHE3, Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3.