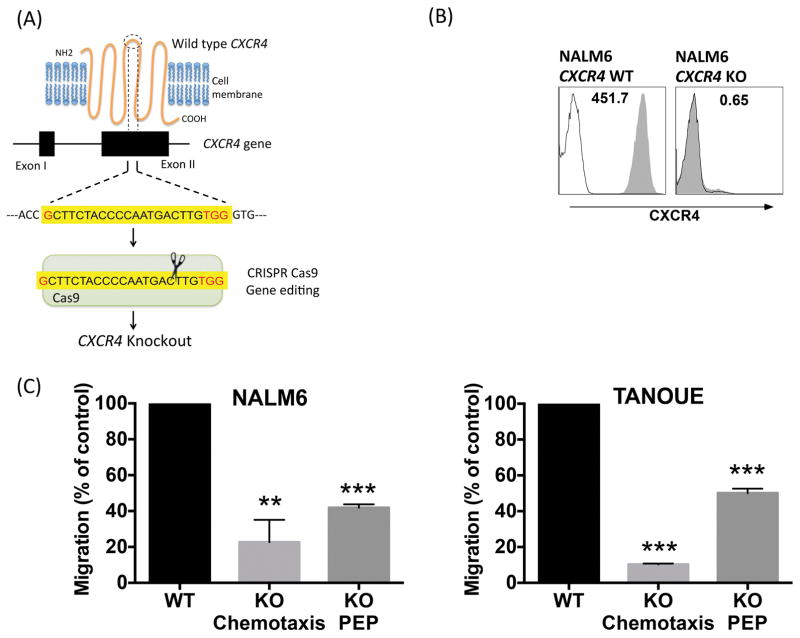
Figure 2. CXCR4 gene deletion significantly decreases chemotaxis and PEP of B-ALL cell lines.
(A) The mechanism of CXCR4 deletion through CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing system. The CRISPR Cas9 was directed towards the second extra cellular loop to introduce a frame-shift mutation resulting in lack of expression of the CXCR4 protein. (B) Histograms depict CXCR4 expression in NALM6 cells before and after CRISPR-Cas9 mediated CXCR4 knockout. Cells were stained with isotype control (black line) or CXCR4 antibody (shaded grey area). (C) NALM6 and TANOUE wild type (WT) and knockout (KO) cells (both untreated) were allowed to undergo chemotaxis towards 100 ng/ml CXCL12 or PEP beneath 9–15C Bone Marrow Stromal Cells and migrated cells were counted in flow cytometer for quantification. Bar diagrams representing mean chemotaxis/PEP (± SEM), with *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001.