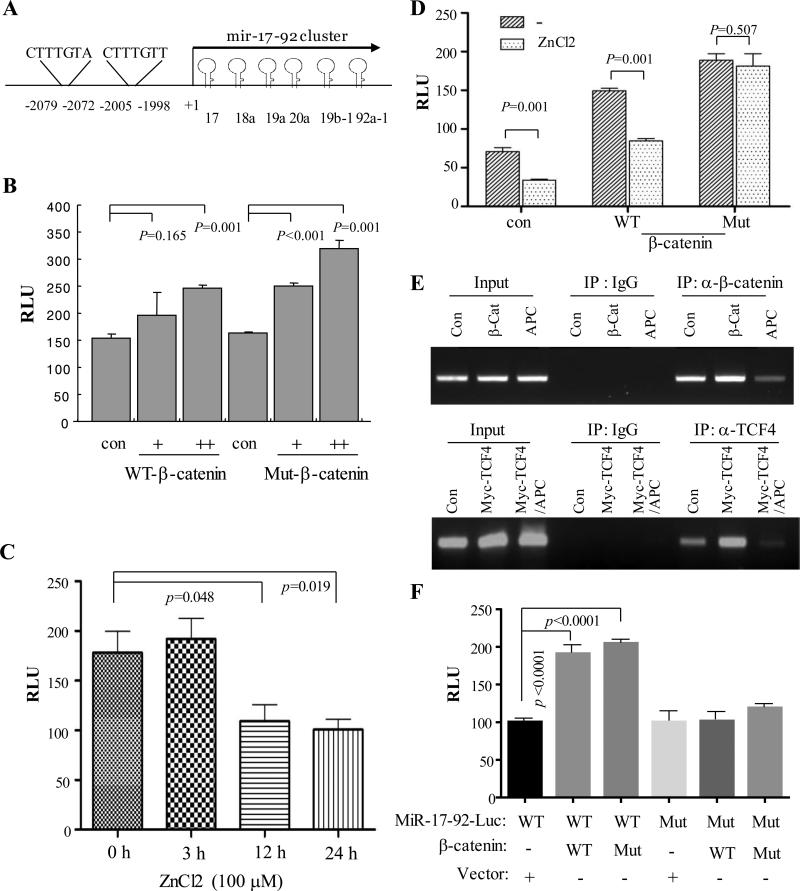
Figure 4. MiR-17-92 promoter is induced by β-catenin which is inhibited by APC.
(A) Diagram represents miR-17-92 promoter with the two TCF/LEF binding sites indicated. (B) β-catenin induces miR-17-92 luciferase promoter activity. HEK293 cells were transfected with pGL3-miR-17-92-Luc together with or without WT and Mut β-catenin. Luciferase assay was performed after 48 h incubation. (C) APC inhibits miR-17-92 promoter activity. pGL3-miR-17-92-Luc was introduced into APC/HT29 cells. Following induction of APC expression by ZnCl2, luciferase activity was measured. (D) APC represses wild-type but not constitutively active mutant β-catenin induced miR-17-92 promoter activity. Luciferase assay was carried out in APC/HT29 cells that were transfected with indicated plasmids and treated with/without ZnCl2. (E) β-catenin/TCF/LEF directly binds to miR-17-92 promoter, which is inhibited by APC. HEK293 cells were transfected with vector control, β-catenin or Myc-TCF4 together with and without APC, and then subjected to ChIP assay with β-catenin and TCF4 antibodies. IgG was used as control. (F) Mutation of TCF/LEF binding sites of the miR-17-92 promoter largely abrogates the miR-17-92 promoter activity induced by β-catenin. Following transfection of wild-type and mutant miR-17-92-Luc together with and without WT and constitutively active Mut β-catenin for 48 h, luciferase assay was performed.