FIGURE 7.
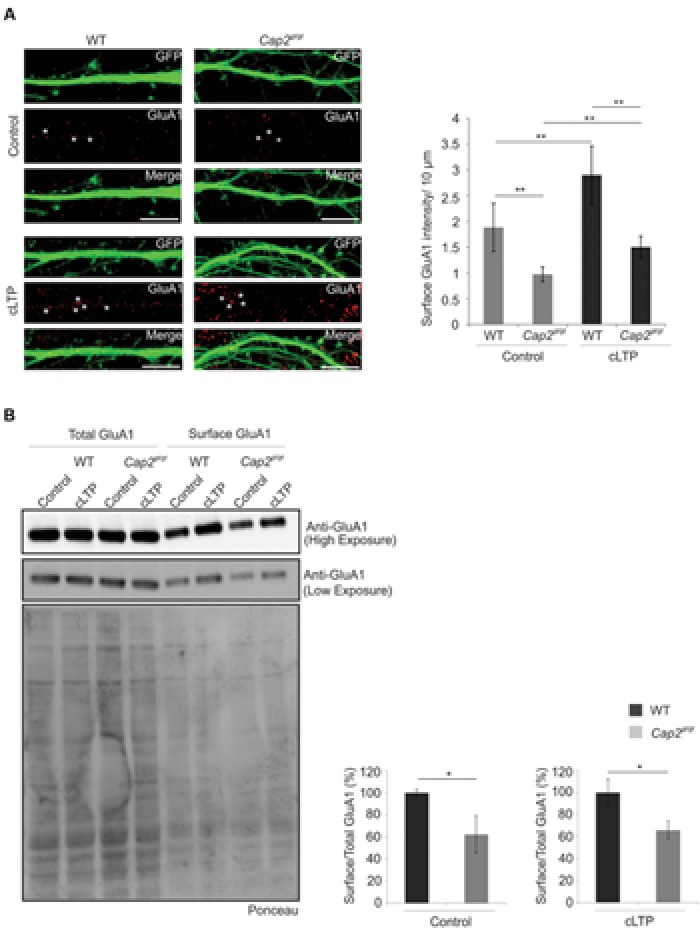
Surface AMPA receptor trafficking is impaired in CAP2 null neurons. (A) pEGFP-C2 transfected WT and CAP2 mutant neurons labeled with antibodies against GluA1 in control and upon cLTP induction. Scale bar, 10 μm. Quantification of data revealed a significant decrease in GluA1 surface intensity in control condition and upon cLTP induction. (WT control: 1.8 ± 0.46 surface GluA1 intensity (AU)/10 μm; Cap2gt/gt control: 0.97 ± 0.14 surface GluA1 intensity (AU)/10 μm; white asterisk; n = 40 neurons from 3 set of different experiments; p < 0.01; WT cLTP: 2.9 ± 0.55 surface GluA1 intensity (AU)/10 μm; Cap2gt/gt cLTP: 1.5 ± 0.2 surface GluA1 intensity (AU)/10 μm; white arrows; n = 40 neurons from 3 set of different experiments; p < 0.01). (B) Surface biotinylation and western blotting with GluA1 in control and cLTP induced cortical neurons. Quantification of data revealed a significant decrease in surface GluA1 in CAP2 mutant neurons in control condition (WT control surface/total: 100 ± 3.2%; Cap2gt/gt control surface/total: 62.3 ± 16.8%; n = 3 neuronal preparations; p < 0.05) and upon cLTP induction (WT cLTP surface/total: 100 ± 12.1%; Cap2gt/gt cLTP surface/total: 65.9 ± 8.3%; n = 3 neuronal preparations; p < 0.05). Ponceau staining of the nitrocellulose membrane as loading control for the pull down assay of surface AMPA. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
