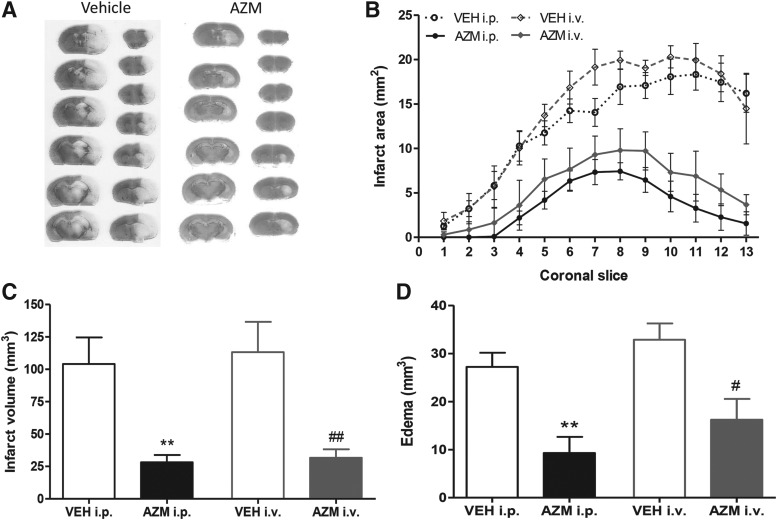
Fig. 3.
Reduction of ischemic brain damage produced by a single i.v. administration of azithromycin is comparable to the neuroprotection observed after i.p. administration of the drug. (A) Representative cresyl violet-stained coronal brain sections from mice subjected to transient MCAo and receiving an i.v. injection of vehicle (saline, 1 mL/kg) or azithromycin (AZM, 150 mg/kg) upon reperfusion. (B) Brain infarct areas (pale areas in A), (C) infarct volume, and (D) edema of mice subjected to transient MCAo and treated i.p. or i.v. with a single dose of azithromycin (AZM, 150 mg/kg) or vehicle (VEH, saline, 1 mL/kg) upon reperfusion. **P < 0.01 versus VEH i.p.; ##P < 0.01 versus VEH i.v.; and #P < 0.05 versus VEH i.v. (two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test, n = 5 mice per experimental group). i.v., intravenous.