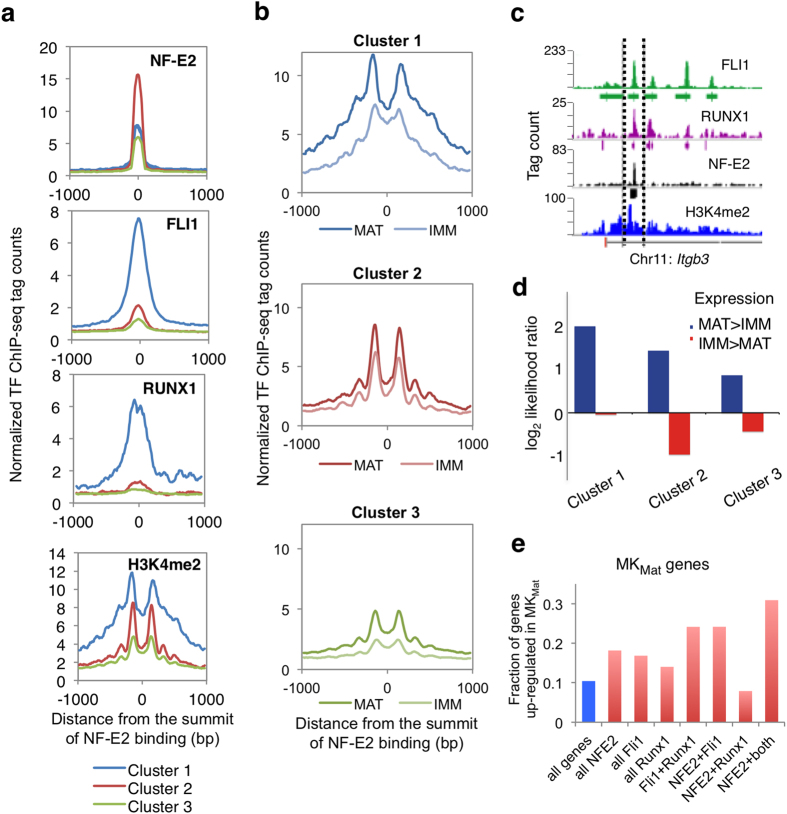
Figure 7. Functional analysis of TF co-occupancy at MK enhancers.
(a) Composite ChIP-seq signals for NF-E2, FLI1, RUNX1, and H3K4me2 at 3 distinct clusters of NF-E2 binding sites, identified by K-means clustering of binding sites for the three TFs and described in the text. (b) Composite ChIP-seq signals for H3K4me2 in MKImm and MKMat at the 3 clusters of NF-E2 binding sites. (c) ChIP-seq data traces at a representative MKMat-specific locus, Itgb3, showing all three TFs occupying a putative regulatory region marked with H3K4me2. Other sites in the locus show binding of one or two TFs. (d) Odds ratios of genes near (<20 kb) NF-E2 binding sites in each cluster showing higher expression in MKMat (blue) or in MKImm (red), relative to the genome background. (e) Proportion of genes with nearby binding of the various combinations of NF-E2, FLI1, and RUNX1 among genes showing higher expression in MKMat. The data indicate the functional role of FLI1, in conjunction with NF-E2 or RUNX1 and especially with both TFs, in regulating genes expressed in mature, but not in immature (Suppl. Fig. 2d) MK.