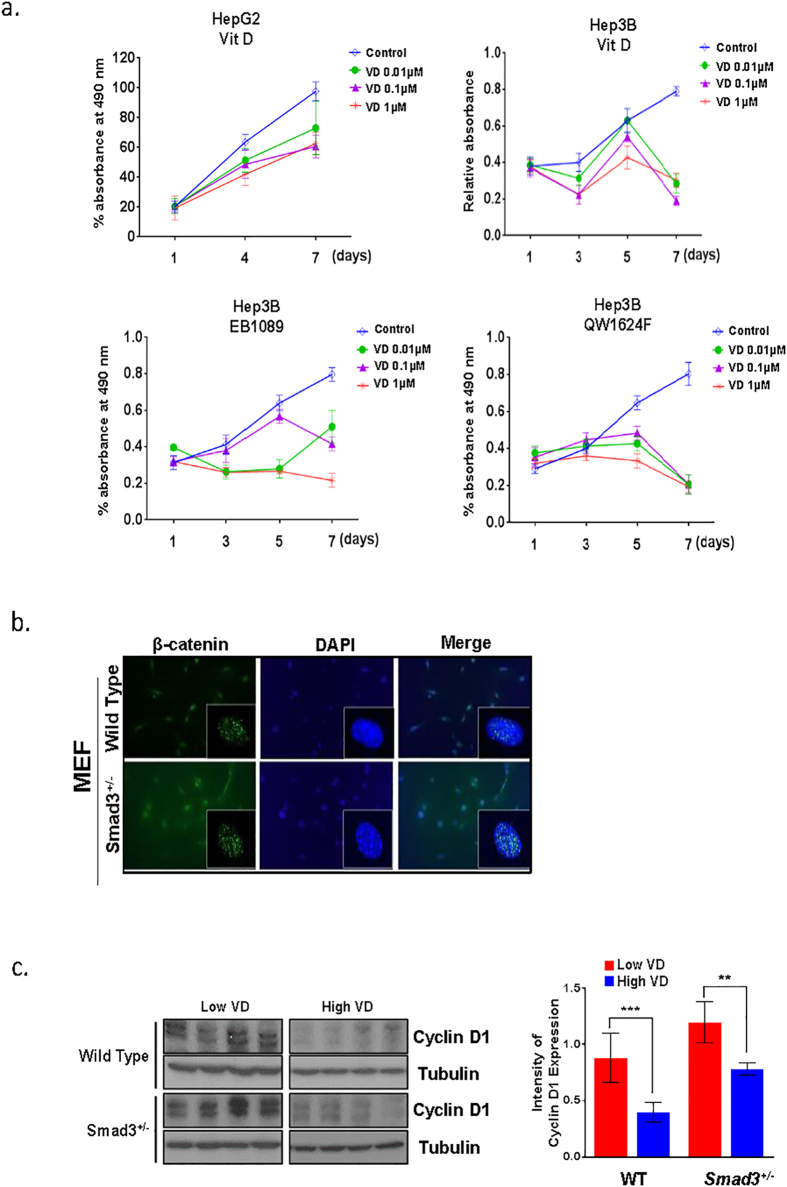
Figure 5. VDR signaling pathway reduces the proliferation rate of liver cancer cells, and loss of Smad3 increased levels of nuclear β-catenin.
(a) HepG2 and Hep3B cells were treated 10 nM, 100 nM or 1000 nM of VD, EB1089, or QW1624F and with control (100% ethanol), and this treatment continued for 7 days. Viability of the cells was assessed on indicated day using MTS reagent (Promega). (b) β-catenin nuclear localization intensity was measured by immunofluorescence staining with phospho-β-catenin antibodies and DAPI in control and Smad3+/− MEF cells. (c) Western blot analysis of cyclin D1 in liver tissue taken from wild type and Smad3+/− mice fed with either high or low VD (4 mice in each group). Intensity of cyclin D1 expression in each group of mice was displayed in bar graph (right panel). (**P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0005, Student’s t-test).