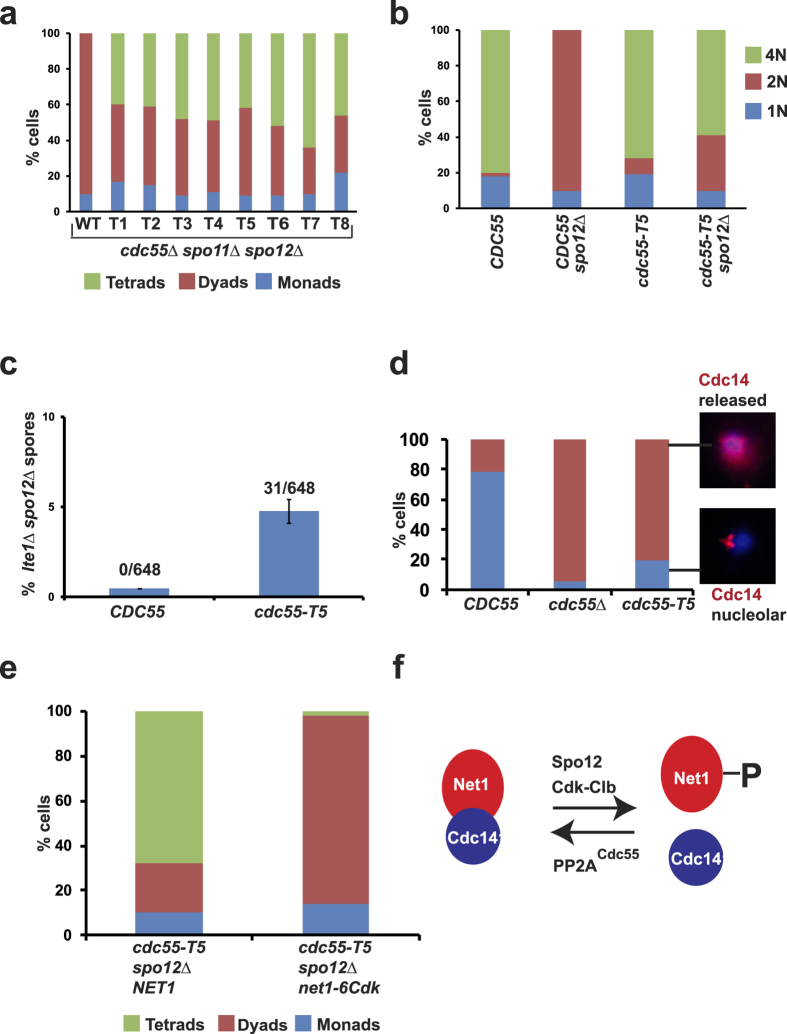
Figure 2. cdc55-T5 mutants release Cdc14 prematurely from the nucleolus.
(a) Class A mutations in cdc55 partially suppress the spo11Δ spo12Δ dyad phenotype. Eight alleles that suppressed dyad phenotype are labelled T1-8 (T = tetrad-forming allele) (N = 100). (b) cdc55-T5 suppresses the nuclear division defect of spo12Δ cells. CDC55 SPO12, CDC55 spo12Δ, cdc55-T5 SPO12, cdc55-T5 spo12Δ cells were induced to sporulate by transferring them to SPM and incubating for 12 hours in a shaker at 30 °C. Cells were stained with DAPI and classified as either mononucleate, binucleate or tri/tetra-nucleate (N = 100). (c) Frequency of lte1Δ spo12Δ haploids produced from sporulation followed by tetrad dissection (216 tetrads each in triplicates) and germination of LTE1/lte1Δ SPO12/spo12Δ diploids carrying either CDC55 or cdc55-T5. Difference in the frequencies between CDC55 and cdc55-T5 strains is statistically significant (Student’s t-test, P < 0.01). (d) PMET3-CDC20 cells carrying either CDC55 or cdc55Δ or cdc55-T5 were transferred to SD medium in the presence of methionine and incubated for 160 minutes. Cells were fixed and subjected to immunostaining with anti-Cdc14 antibodies. DNA was visualized by staining with DAPI. Percentage of cells with nucleolar Cdc14 and released Cdc14 signals were calculated (N = 100). Representative images of cells with nucleolar and released Cdc14 signals are shown. (e) cdc55-T5 NET1 spo12Δ and cdc55-T5 net1-6Cdk spo12Δ strains were induced to sporulate by transferring them to SPM followed by incubation for 24 h. Spores were harvested and nuclear division was scored by staining with DAPI (N = 100). (f) Antagonistic roles of PP2ACdc55 and Spo12 in the regulation of FEAR pathway.