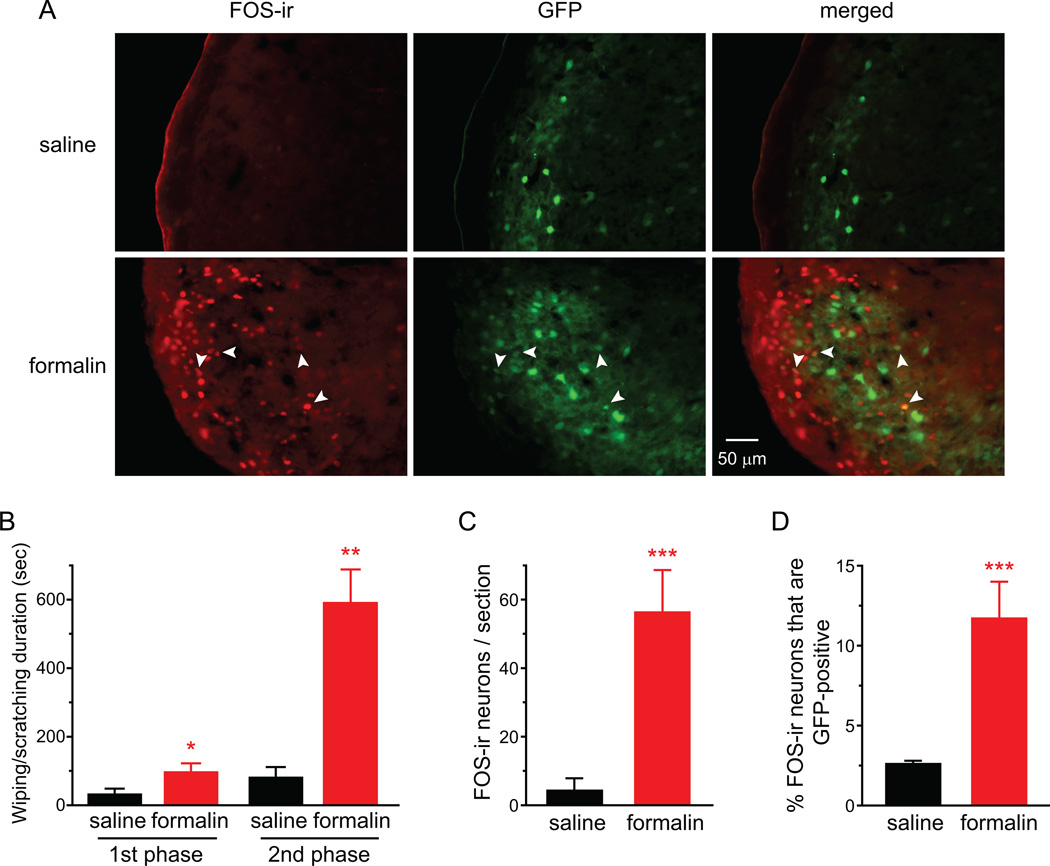
Fig. 5. Facial formalin injection induces FOS expression in inhibitory neurons in TCC.
(A) Representative images of FOS-positive cells and GFP-positive cells in caudal Vc of heterozygous GAD67-GFP mice that received saline or 1% formalin injection into the periorbital skin. Arrows indicate FOS-ir in GFP-positive cells.
(B) Total duration of nocifensive behavior in response to intradermal injection of 20 µl saline or 1% dilute formalin at the periorbital region of heterozygous GAD67-GFP mice. The 1st and 2nd phases include behavior 0–10 min and 10–60 min after injection, respectively (n = 3 mice in each group; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, two-tailed t-test, compared with the corresponding saline group).
(C) Average number of FOS-positive TCC neurons in heterozygous GAD67-GFP mice that received periorbital injection of saline and formalin, respectively (same mice as in B; ***p < 0.001, two-tailed t-test).
(D) The percentage of FOS-positive neurons that are GFP-positive (same mice as in B; ***p < 0.001, two-tailed t-test).