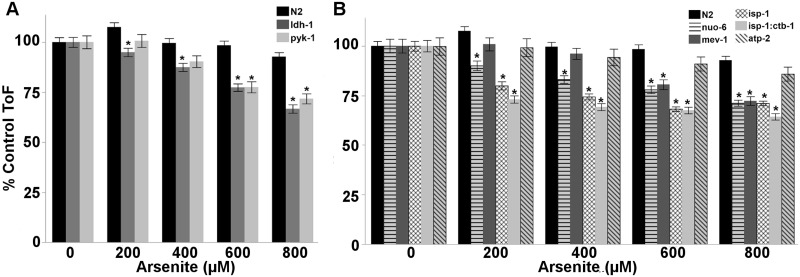
FIG. 6.
Deficiencies in glycolysis and ETC genes sensitize nematodes to arsenite. Nematodes deficient in (A) pyruvate kinase and lactate dehydrogenase (two way ANOVA, main effects of strain, arsenite and their interaction (P < 0.0001 for all)), as well as (B) ETC complexes I (nuo-6), II (mev-1), and III (isp-1; isp-1:ctb-1), but not ATP synthase (atp-2), are sensitive to arsenite exposure (two way ANOVA, main effects of strain, arsenite and their interaction (P < 0.0001 for all)) in a 48 h larval growth assay. As nematode strains develop at varying rates, all ToF (surrogate for nematode length) data is normalized to percent growth of control. Raw ToF data is shown in Supplemental Figures S9 and S10. Asterisk denotes statistical significance (P < 0.05) for post-hoc (Tukey’s HSD) comparison to N2 within each arsenite concentration, and are listed in Supplemental File 1. N = 166–406. Bars ± SEM.