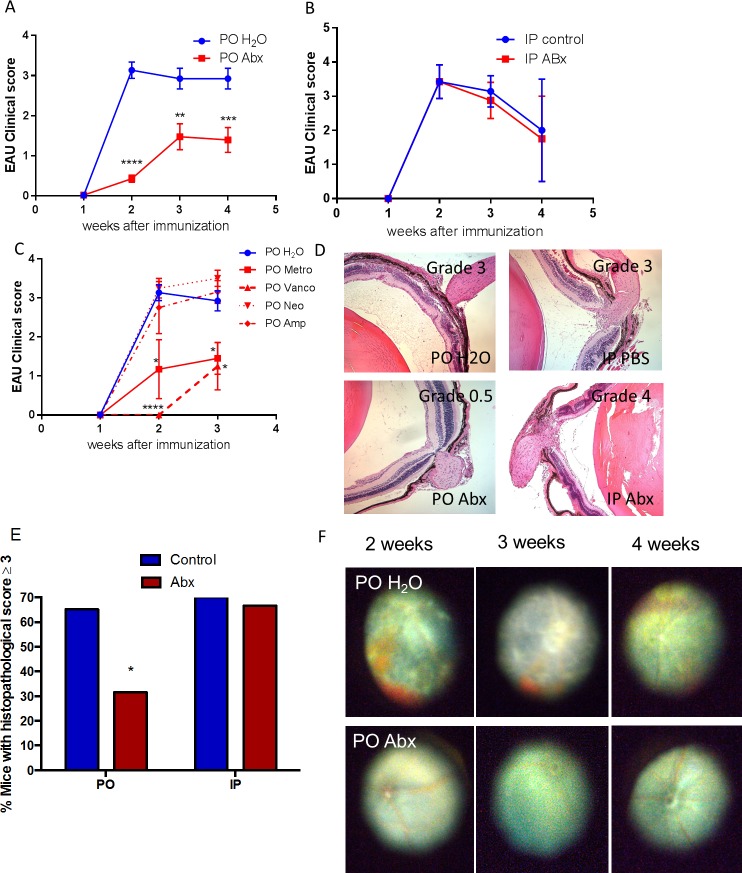
Figure 1.
Broad-spectrum PO but not IP antibiotics reduce the severity of EAU in B10.RIII mice. (A) Experimental autoimmune uveitis clinical score over 4 weeks in water-fed (PO H2O) versus quadruple-antibiotic-fed (PO Abx) mice (ampicillin [1g/L] [Amp], neomycin [1 g/L] [Neo], metronidazole [1g/L] [Metro], and vancomycin [500 mg/L] [Vanco]) ad libitum starting 1 week before immunization. (B) Experimental autoimmune uveitis clinical score over 4 weeks in mice treated with either IP PBS (IP control) or daily broad-spectrum IP antibiotics (IP Abx). (C) Experimental autoimmune uveitis clinical score when four antibiotics used above were given singly, compared with water. (D) Retinal histologic grading of control (top) vs antibiotic-treated (PO or IP Abx) animals (bottom). (E) Chi-square analysis of histologic grading at 3 weeks postimmunization. (F) Fundus photos of immunized mice when given regular drinking water (top) compared with broad-spectrum antibiotics (bottom) at 2 to 4 weeks after immunization; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; n = 5 to 39 animals per time point for clinical scoring; n = 9 to 12 per treatment group for histologic scoring (remaining eyes used for retinal whole mounts or flow cytometry) (± SEM shown).