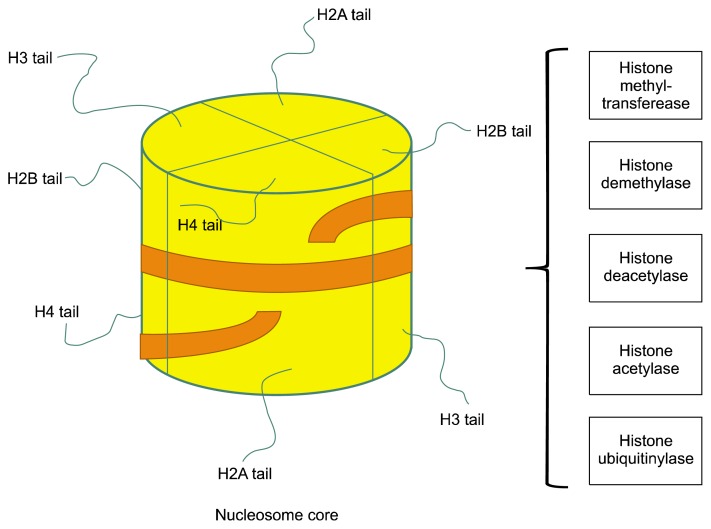
Fig. 1.
Schematic of nucleosome structure. Nucleosomes are the smallest structural unit of chromatin. Nucleosome consists of two copies of each core histone (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) and ~150 bp DNA. The N-terminal tail of each histone is extruded from the nucleosome. Amino acids in histone tails can be modified by numerous enzymes bringing acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination and other substitutions, creating a complex ‘bar’ code, which may influence chromatin structure by affecting histone-histone and histone-DNA interactions. Post-translational modifications of histones regulate transcription of genes important for self-renewal and differentiation.