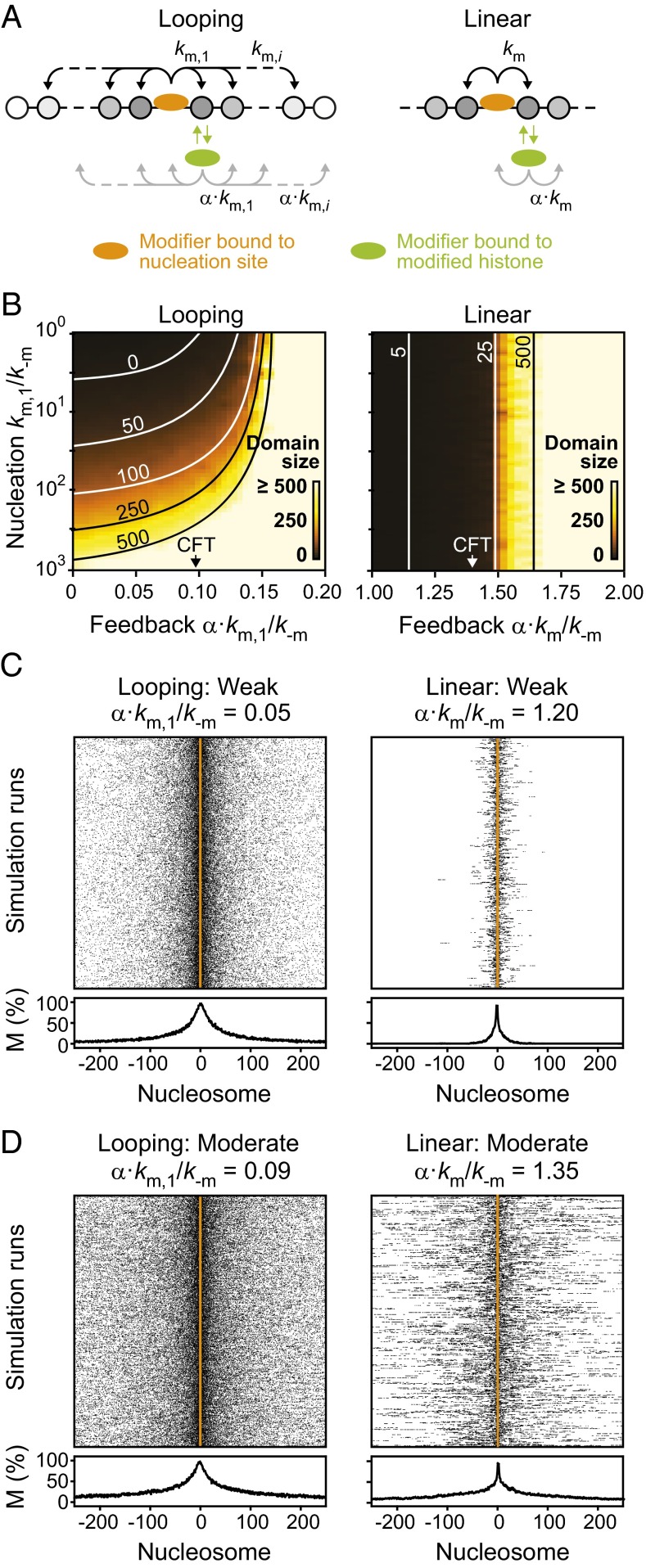
Fig. 3.
Influence of nucleation and feedback strength on domain size. (A) Trans-acting modifiers can propagate the modification via positive feedback. Due to the different affinity for modified nucleosomes compared with nucleation sites, the rates were scaled with a factor α. In the looping model (Left), bound modifiers can modify nucleosomes beyond the next neighbor, whereas only next neighbor contacts are considered in the linear spreading model (Right). (B) Resulting domain sizes as a function of nucleation and feedback strength. Lines indicate parameter combinations that yield the indicated domain size. (C and D) Spatial distribution of modified nucleosomes across the simulated domain for weak (C) and moderate (D) feedback strengths. See Fig. S2 for strong feedback.