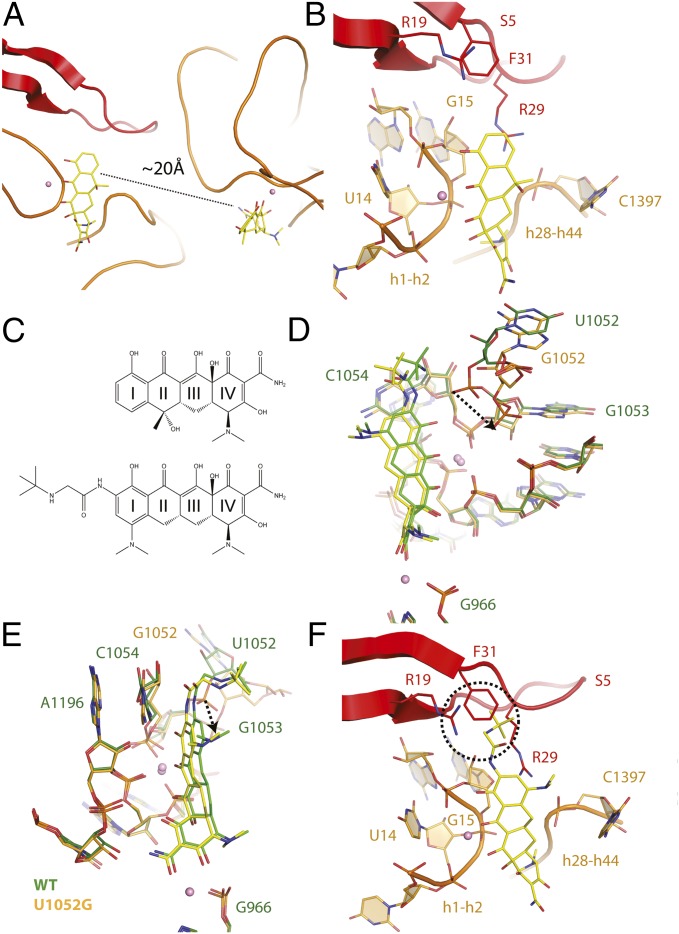
Fig. 4.
Two tetracycline binding sites are present in mutant U1052G. (A) Presence of two tetracycline binding sites in the U1052G mutant. (B) The novel tetracycline binding site is located near the highly conserved 16S central pseudoknot and adjacent to the previously established streptomycin binding site. (C) Chemical structures of (Upper) tetracycline and (Lower) tigecycline. (D) Superposition of the tetracycline-bound crystal structures of the wild-type and U1052G mutant ribosome. The dotted arrow represents the displacement of the phosphate group of nucleotide G1053 in the U1052G mutant. (E) This panel is rotated 90° along the vertical axis. (F) Tigecycline modeled into the second tetracycline binding site of U1052G. The dotted circle illustrates the expected steric clash between the butylglycylamido substituent attached to Ring I of tigecycline with residues found in the S5 protein. In these panels, wild-type is green, and the U1052G mutant is yellow. Magnesium ions are shown as pink spheres.