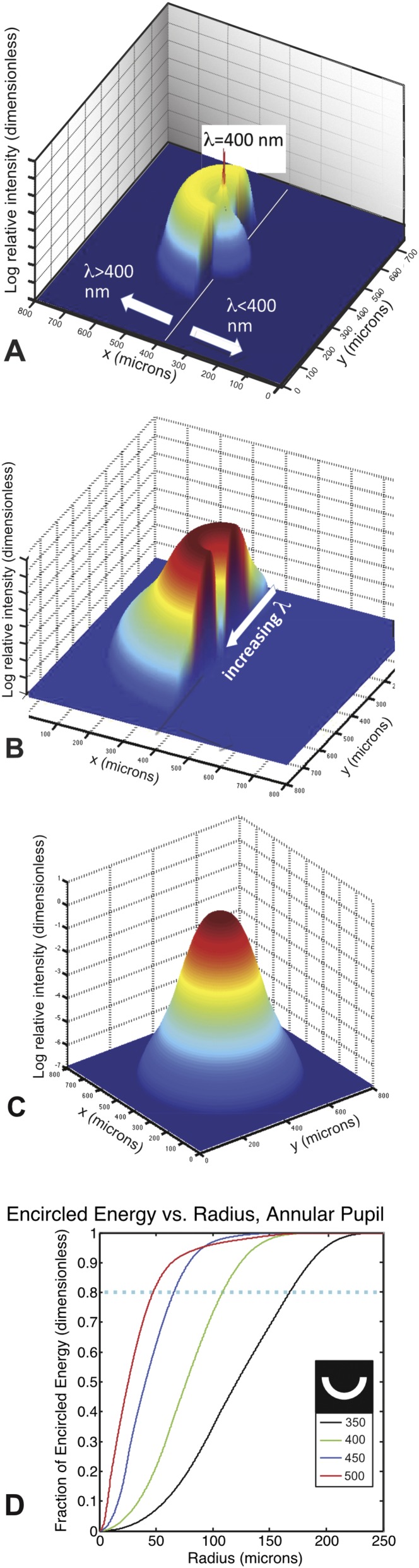
Fig. S4.
PSF and encircled energy results from chromatic aberration computations. (A) Chromatic PSF for 400-nm best focus, semiannular pupil. This figure shows the computed photon intensity on the retinal surface for a point source at infinity, with a solar spectrum filtered to a 3-m depth, convolved with the opsin sensitivity function. The spatial units are micrometers. This PSF is for the half-annular pupil geometry, so that light with λ > 400 nm has yet to come to a focus, whereas light with λ < 400 nm has already passed through its position of best focus. The spike at the center corresponds to the best focused photons with λ = 400 nm, which have the highest surface brightness. (B) Chromatic PSF for 700-nm best focus, semiannular pupil. This PSF is computed for the same half-annular pupil as in A, but the PSF has been rotated about the optical axis by 180° for clarity. All of the rays have passed through their position of best focus, and therefore, there is a monotonic relationship between wavelength and distance from the axis of symmetry as indicated. The radial plot of photon surface brightness amounts to a dispersed spectrum of the incident light, with the redder light being closest to being in focus. (C) Chromatic PSF for 700-nm best focus, full pupil. As distinct from the semiannular case, the center of the PSF is filled in with polychromatic light that passes through the center of the pupil and suffers minimal chromatic blurring, whereas the outer edges of the PSF are illuminated exclusively by the photons of the shortest wavelength. There is, therefore, a radial gradient in spectral purity and a complex relationship between position and spectral content. (D) Encircled energy vs. radius for various accommodation settings. This result is for the semiannular pupil at different accommodation settings indicated as the best focus wavelength in nanometers. The plot shows the integrated enclosed energy within the PSF for the semiannular pupil geometry. This result was computed for a white reflector illuminated by the depth-attenuated solar photon spectrum for 350 < λ < 650 nm. The red curve yields an 80% encircled energy radius of 47 μm, which corresponds to a Gaussian–PSF-equivalent FWHM of 61 μm at the accommodation setting of sharpest focus, which corresponds to a best focused wavelength of 500 nm.