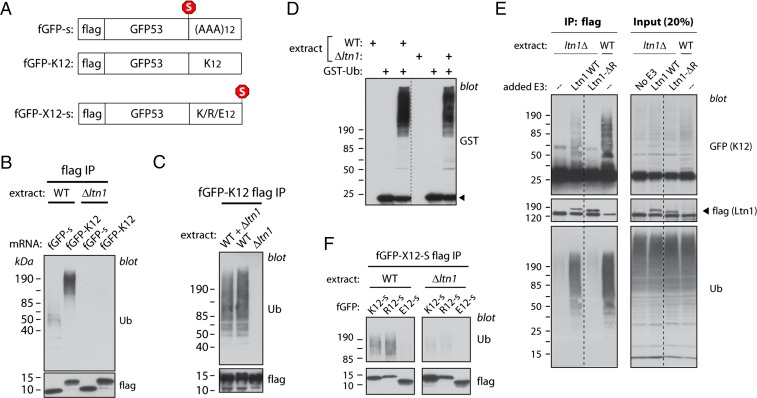
Fig. 1.
Newly synthesized NSPs are ubiquitylated in Neurospora extracts in an Ltn1-dependent manner. (A) Diagram of templates used for in vitro translation, encoding flag-GFP53 (fGFP-s), the equivalent nonstop protein (fGFP-K12), equivalent proteins fused to homopolymeric tracts of 12 lysines (fGFP-K12-s), arginines (fGFP-R12-s), or glutamates (fGFP-E12-s); “s” indicates that the encoding mRNA harbor four in-frame stop codons. (B) Nonstop proteins synthesized in Neurospora extracts become ubiquitylated in an Ltn1-dependent manner. Three hundred nanograms of mRNA encoding fGFP-s or fGFP-K12 reporters were used to program translation reactions (30 μL) prepared from WT or Ltn1-deficient (Δltn1) strains for 30 min. Reaction products denatured with 1% SDS were diluted 10-fold and used for immunoprecipitation (IP) using anti-flag antibody. IPed proteins were used for immunoblots against ubiquitin (Ub) or flag. (C) The NSP ubiquitylation defect of Ltn1-deficient extracts is not due to the presence of trans-acting inhibitors. fGFP-K12 was synthesized in WT or Δltn1 extracts, or in a 1:1 WT:Δltn1 extract mixture. Reaction products were analyzed for ubiquitylation as in B. (D) Ltn1-deficient extracts are competent for de novo ubiquitylation. WT and Δltn1 extracts were incubated with GST-tagged ubiquitin (GST-Ub; 10 μM) in the presence of 1 mM ATP for 10 min at 26 °C as indicated, and the ligation of GST-Ub to proteins in the extract (as revealed by the formation of a smear) was examined by anti-GST immunoblot. The arrowhead indicates free GST-Ub. Dashed lines indicate that lanes were removed from the original image. (E) Recombinant Ltn1 restored NSP ubiquitylation activity to Δltn1 extracts. Recombinant, flag-tagged WT yeast Ltn1 or a mutant lacking the catalytic RING domain (Ltn1-ΔR) was added at 40 nM to Δltn1 extract, as indicated, before translation using 300 ng of fGFP-K12-encoding mRNA (full-length GFP used for this experiment). Ubiquitylation of fGFP-K12 was measured as in B. Dashed lines indicate that lanes were removed from the original image. (F) Proteins encoded by stop codon-containing mRNA, but harboring polybasic tracts, are targeted by Ltn1. WT or Δltn1 extracts were programmed with 300-ng templates encoding fGFP appended with a C-terminal tract of 12 Lys, Arg, or Glu, as represented in A. Reaction products were analyzed for ubiquitylation as in B.