Figure 1.
Image Preprocessing, Registration, and NBLAST Algorithm
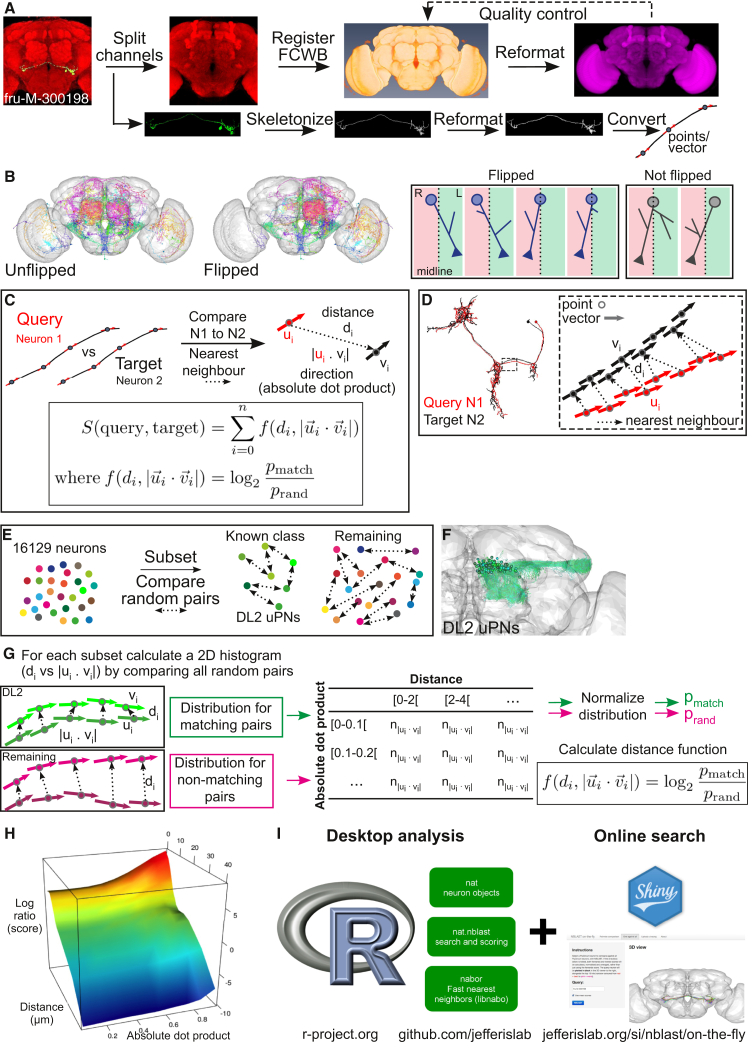
(A) Flowchart describing the image preprocessing and registration procedure. FlyCircuit images were split into two channels. The Dlg-stained brain (Discs large) images were registered against the FCWB template. Successful registrations were applied to neuron skeletons converted into points and vectors.
(B) Neurons in the right hemisphere were flipped to the left. Brain plots show 50 random neurons before and after flipping. On the right, cases for which the neuron flipping was assessed manually.
(C) NBLAST algorithm. The similarity of two neurons (query and target) is a function of the distance and absolute dot product between nearest-neighbor segments of the query/target pair. This function reflects the probability of a match between a pair of segments (pmatch) relative to a random pair (prand).
(D) Diagram illustrating how nearest-neighbor points are calculated. For a query (N1)/target (N2) pair, each point of N1 (ui) is matched to a point in N2 (vi), minimizing the distance (di).
(E) Defining the scoring function. Random pairs of neurons within two groups, DL2 uPNs and all remaining neurons, were compared.
(F) Brain plot of DL2 uPNs.
(G) Calculation of the distribution for matching and non-matching pairs of segments. For all segment pairs of all neuron pairs in each group, the distance and a 2D histogram were calculated for absolute dot product (10 bins) and distance (21 bins). These histograms were converted to joint probability densities for matching (pmatch) or non-matching pairs (prand) by normalizing the distance histogram to sum to 1.
(H) Plot showing that similarity score depends on distance between points and the vector direction (absolute dot product).
(I) Summary diagram of the desktop and online NBLAST implementation.