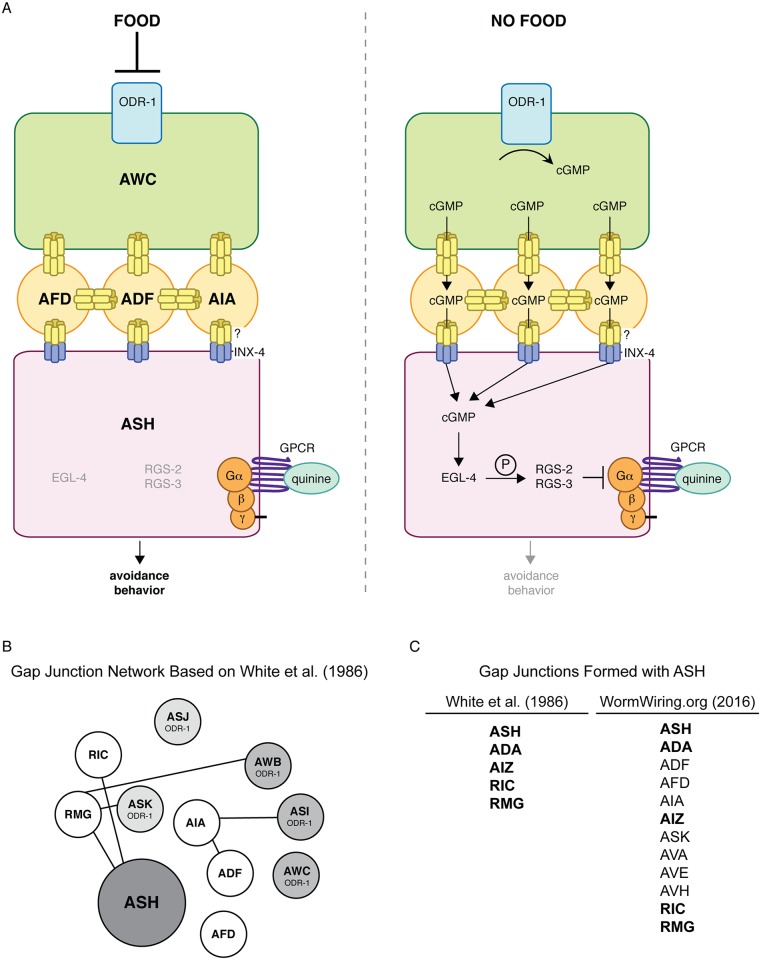
Fig 8. Model for ODR-1 modulation of ASH-mediated nociceptive signaling.
(A) Our working model is that the transmembrane guanylyl cyclase ODR-1 functions in the AWB, AWC and ASI sensory neurons to decrease C. elegans behavioral sensitivity to the bitter tastant quinine (and possibly the volatile odorant octanol). Removal of food leads to cGMP accumulation, at least in the AWCs, likely by direct/indirect activation of ODR-1 in these neurons. Based on the re-annotated wiring diagram (WormWiring.org), we propose that cGMP then flows via gap junction connections from the site of its production in the ODR-1-expressing AWB/AWC/ASI sensory neurons, through ADF, AFD and AIA, to the ASH nociceptors. Once in ASH, cGMP activates the cGMP-dependent protein kinase EGL-4, which likely directly phosphorylates the regulator of G protein signaling proteins RGS-2 and RGS-3, stimulating their activity [58]. RGS-2 and RGS-3 downregulate Gα proteins that signal downstream of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that are activated by ligands such as quinine and octanol. When animals are well-fed, cGMP levels are low and there is only minimal inhibition of G protein-coupled signaling in ASH. Upon food remove, cGMP influx into ASH activates EGL-4, resulting in diminished nociceptive behavioral sensitivity to a subset of ASH-detected aversive stimuli. Decentralized modulation of ASH sensitivity may allow an animal to integrate multiple environmental cues with its internal state to maximize the appropriateness of its response to its surroundings. (B) The same diagram depicted in Fig 5A is shown here, but with only those gap junction connections originally reported in White et al. [2] included. (C) The left column shows a list of the neurons reported by White et al. [2] to make gap junctions with ASH, while the right column lists the neurons currently annotated at WormWiring.org to make gap junctions with ASH. The neurons shown in bold are those that are common to both lists.