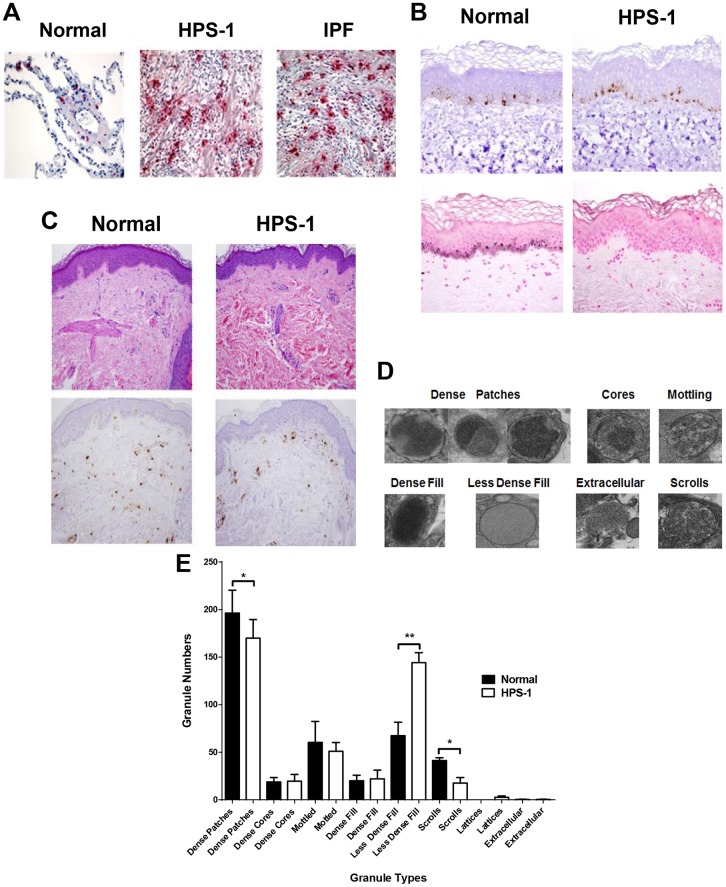
Fig 1. Pulmonary mast cells localize to fibrotic regions of the lung parenchyma in HPS-1 pulmonary fibrosis. Histology, immunohistochemistry and ultrastructure of HPS-1 derived dermal mast cells.
A) Representative anti-tryptase stained lung sections from patients with HPS-1 pulmonary fibrosis and IPF showed significant numbers of pulmonary mast cells within fibrotic alveolar interstitium. Mast cells are shown in normal lung tissue for comparison. Data are representative of four separate patients with either HPS-1 or IPF; B) Staining of skin biopsies reveals normal numbers of melanocytes (Melan-A) (upper panels) but decreased melanin pigmentation (Fontana-Masson) in HPS-1 patients (lower right panel; compare with lower left panel); (C) Wright-Giemsa staining (upper panels) and tryptase staining (lower panels) of dermal mast cells; (D) Ultrastructure of normal and HPS-1 HuMC granules used for classification include dense patches, cores, mottling, dense fill, less dense fill and extracellular patterns, with or without scrolls or lattices, and E) Comparison of normal and HPS-1 granules showed dense patches with scrolls were significantly increased in normal mast cell granules as compared with less dense fill increased in HPS-1 granules, when granules were scored by three independent observers blinded to the identity of originating mast cells. Data are the means ± SEM (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.