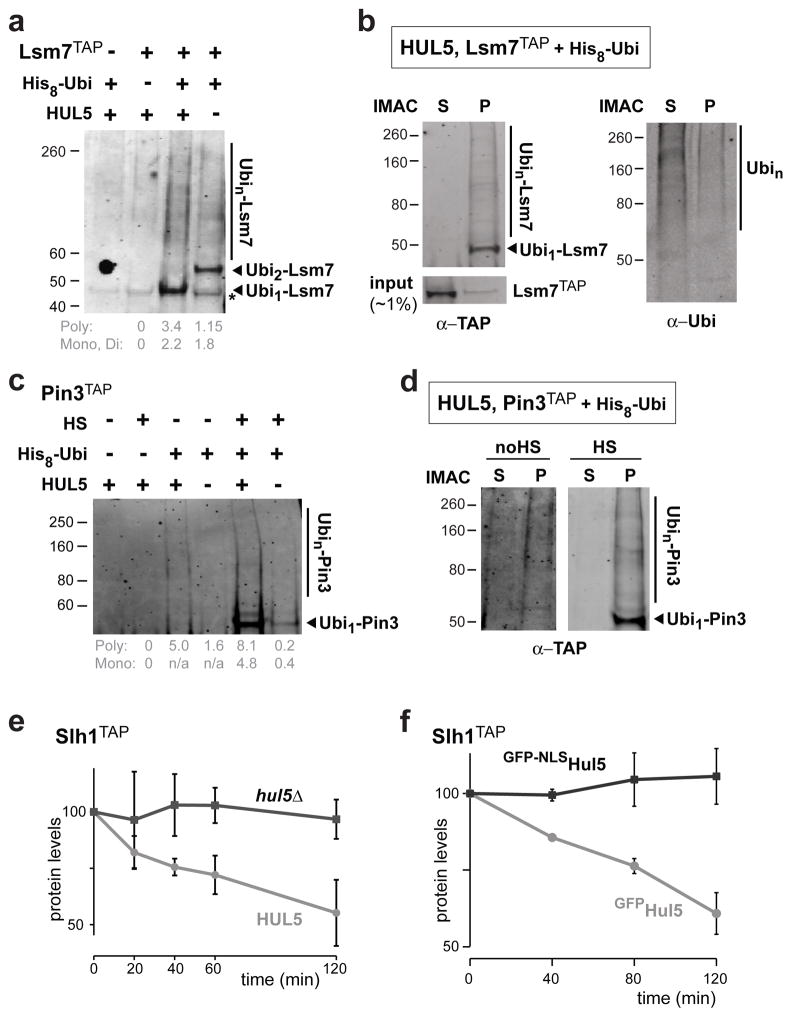
Figure 7.
Hul5 targets proteins that are specifically ubiquitylated in the low solubility cellular fraction. (a–d) Validation of the Hul5 substrate candidates Lsm7 and Pin3 using TAP-tagged strains expressing H8-Ubi. IMAC was performed in denaturating conditions to pull down ubiquitylated proteins, and anti-TAP or anti-ubiquitin antibody was used for Western blot analysis. The asterisk denotes unspecific signal. Corresponding signal intensities for poly- and mono-ubiquitin were measured by subtracting the background signal in control cells (a, c). Solubility of ubiquitylated Lsm7TAP (b) and Pin3TAP (d) were assessed by comparing both soluble and pellet fractions subjected to IMAC and analyzed by Western blots with anti-TAP (b, d) and anti-ubiquitin (b). A 20 min 45°C heat-shock (HS) was also applied to Pin3TAP expressing cells (c, d). (e–f) Turnover of Slh1 is dependent on cytosolic Hul5. Protein levels of Slh1TAP were monitored by Western blot after the addition of 100 μg/ml cycloheximide to both HUL5 and hul5Δ cells grown at 25°C (e), and to hul5Δ cells expressing either GFPHul5 or GFP-NLSHul5 and shifted to 38°C (f). Relative averaged signal intensities (with standard deviations) were quantified and normalized to Pgk1 levels in three independent experiments.