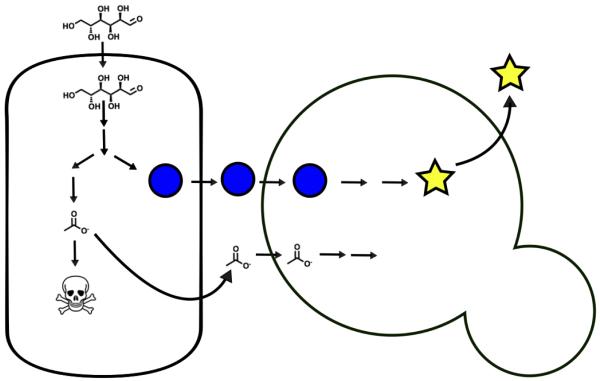
Figure 4.
Coordinating multi-microbe metabolism. Multiple organisms can be coordinated through chemical exchanges and metabolism to produce a desired compound. Here the organism on the left eats glucose and has been engineered to produce the blue circle, but also produces toxic acetate as a byproduct. The organism on the right further converts the blue circle into the end product (yellow star) and also eats the toxic acetate thereby promoting the growth of the organism on the left. Due to their linkage through acetate, the organisms are mutually dependent upon one another for optimal growth.