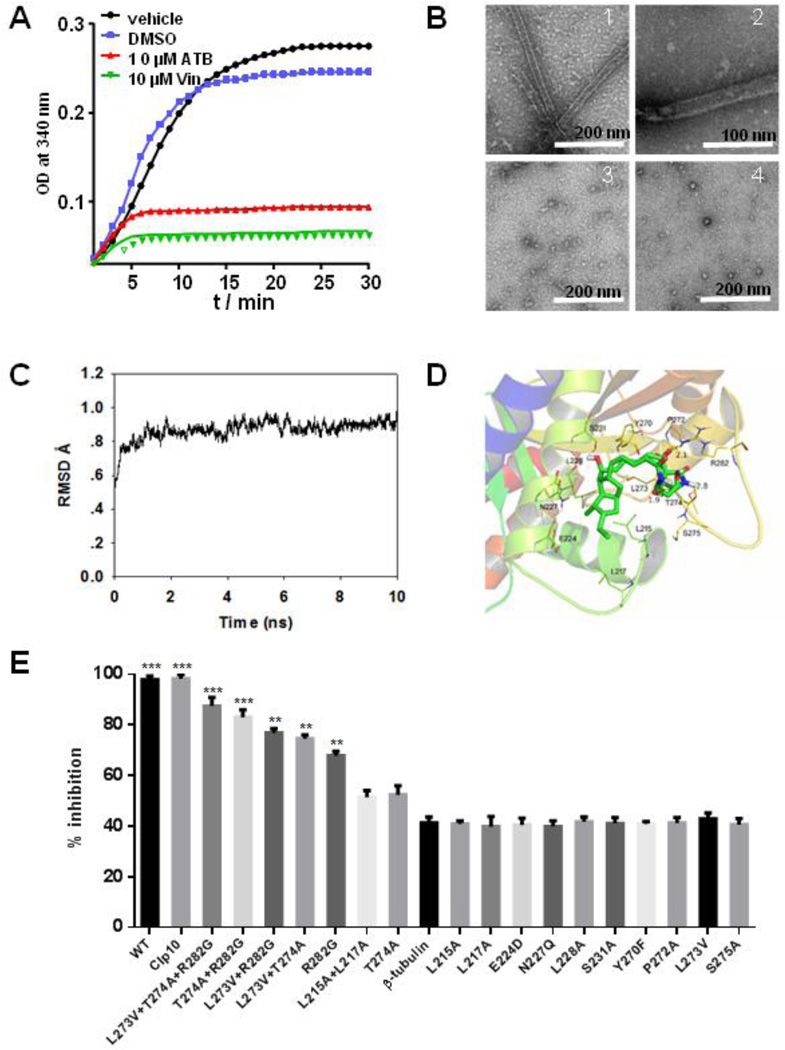
Fig. 3.
ATB inhibits the polymerization of β-tubulin. The tubulin from porcine brain was incubated at 37 °C in the presence of DMSO, 10 µM ATB and 10 µM vincristine, respectively, and tubulin polymerization was measured by taking readings every 30 s for 30 min. Absorbance at 340 mm was monitored in the spectrophotometer (A). Influence of ATB on tubulin polymerization in vitro observed by TEM. ATB was added to tubulin at a concentration of 2 µM. Tubulin incubated with 2 mM GTP, 5% glycerol (B1); 2 mM GTP, 5% glycerol and DMSO (B2); 2 mM GTP, 5% glycerol and 10 µM ATB (B3); 2 mM GTP, 5% glycerol and 10 µM vincristine (B4). The samples (5 µL) were placed on carbon-coated copper grids at the room temperature, fixed for 1 min and negatively stained with 2% uranyl acetate. Grids were air-dried and observed under a transmission electron microscope at 80 kV. Scale bar is 200 nm for (B1), (B3), (V4) and 100 nm for (B2) (B). The ATB was equilibrated after 10 ns MD simulation to produce the plot of RMSD (in ångstrom) of the ATB (C); The detailed interactions between ATB and β-tubulin. ATB selectively binds to the twelve residues of the β-tubulin, namely L215, L217, E224, N227, L228, S231, Y270, P272, L273, T274, S275 and R282 (D); The residues L215, L217, L273, L274 and R282 of β-tubulin may be the binding sites for ATB. The effects of 6.25 µM ATB on the mutants of C. albicans were measured and calculated as follows: % Inhibition = (A570control cells −A570treated cells)/(A570control cells − A570blank cells) × 100. The percentages of inhibition were calculated using software Prism 6. *** indicated P < 0.001 (E).