Figure 7.
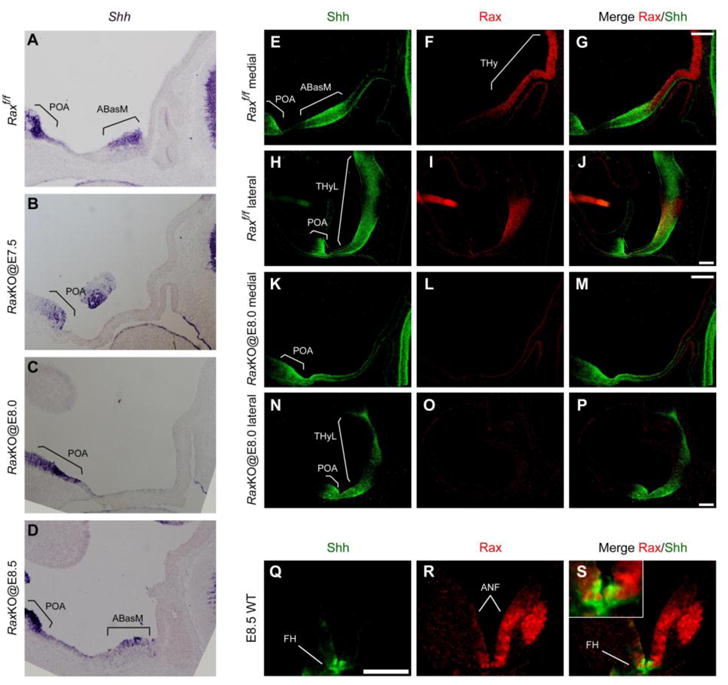
Rax is essential for anterior hypothalamic expression of Shh. (A–D) In situ hybridisation analysis of Shh mRNA expression on midsagittal hypothalamic sections of E11.5 in control (A) and RaxKO embryos injected with tamoxifen at E7.5 (B), E8.0 (C) and E8.5 (D). Note that Shh expression is lost upon Rax gene deletion when tamoxifen is injected at early (E7.5, E8.0) but not later (E8.5) stages. (E–P) Immunofluorescence detection of Shh (green) and Rax (red) expression on midsagittal and lateral sections of E10.5 control (E–J) and RaxKO@E8.0 (K–P) embryos. Shh expression is observed in the preoptic area (POA) of the telencephalon and in the ABasM (medial sections, E–G) and lateral THy (THyL, lateral sections, H–J) within the hypothalamus. Shh expression is lost from the ABasM in RaxKO@E8.0 embryos, but is mantained in the POA and THyL of the same embryos (H–J, N–P). (Q–S) Immunofluorescence detection of Shh (green) and Rax (red) expression on transversal sections of a wild-type E8.5 embryo. The merged image and inset (S) shows that the Shh expression domain, corresponding to the future ventral hypothalamus (FH), is contained within the broad domain of Rax expression in the anterior neural fold (ANF) at this stage. Scale bars 100 μm.
