Figure 3. Effects of chronic stress on epigenetic regulation of the gene encoding CB1 (CNR1).
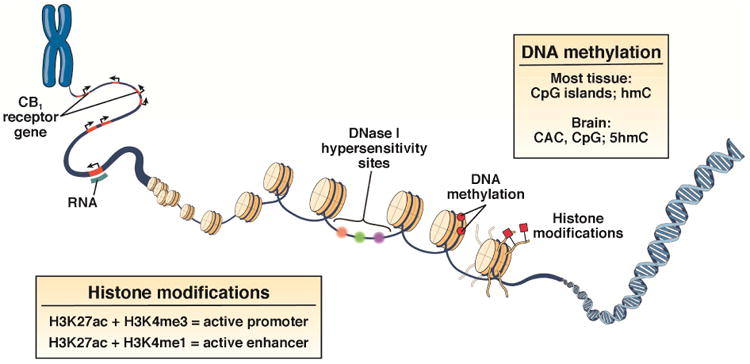
Chromosomes are located in chromatin-bound territories in the nucleus. Euchromatin is characterized by DNase 1 hypersensitivity and specific combinations of histone marks that define active genomic regulatory elements, such as promoters H3K27ac + H3K4me3, and enhancers H3K27ac + H3K4me1. An enhancer can either increase or decrease transcription. Recent research demonstrates that, in brain, the DNA sequence CAC is a common site of methylation, in contrast to other tissues where CpG is most often methylated. Additionally, in brain, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), a reactive species, is methylated. In contrast, in the periphery, methylcytosine (hmC) is a common site for methylation. DNA methylation is catalyzed by DNMTs. Chronic stress is associated with increased levels of DNMT1-mediated methylation of CRN1, resulting in reduced expression. H3K4me3, histone H3 trimethyl Lys4; H3K27ac, histone H3 Lys27 acetylation; H3Kme1, histone H3 monomethyl Lys4. Adapted from Wiley et al.117
