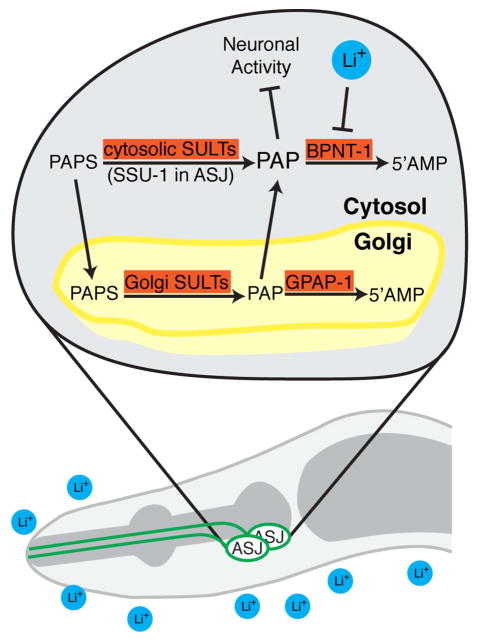
Figure 4. Lithium selectively inhibits the ASJ neurons of C. elegans through inhibition of BPNT-1.
We hypothesize that inhibition of the cytosolic PAP phosphatase BPNT-1 by lithium or genetic mutation leads to a buildup of toxic PAP, due to ASJ-specific expression of the cytosolic sulfotransferase SSU-1. PAP, in turn, causes alterations in cell morphology, transcription, and behavioral outputs of the ASJ neurons. BPNT-1 can also degrade PAP transported into the cytosol from the Golgi, which may explain the synthetic lethality between BPNT-1 and the Golgi-resident PAP phosphatase GPAP-1.