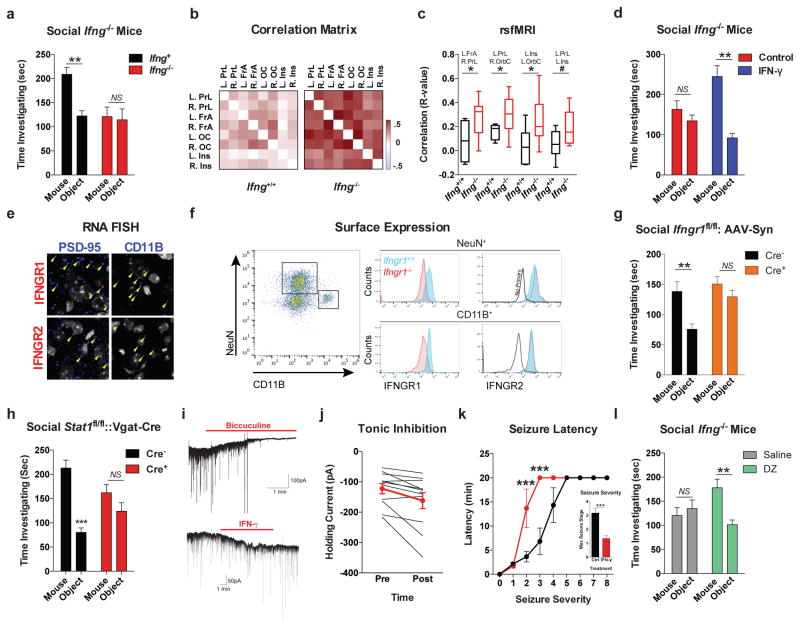
Figure 2. IFN-γ supports proper neural connectivity and social behavior.
a, Ifng−/− mice exhibit social deficits (n = 16;12 mice per group; ANOVA for genotype (F(1, 52)) = 8.327, P < 0.01; **P < 0.01 Sidak’s post-hoc; pooled 2 independent experiments). b, Correlation matrix from Ifng+/+ and Ifng−/− mice. c, Box and whisker plots of correlation values (n = 8 mice per group; *P < 0.05; # P = 0.06 t-test; repeated 2 times). d, A single CSF injection of IFN-γ (20ng) was sufficient to rescue social deficits in Ifng−/− mice 24 hours post-injection (n = 14;11 mice per group; ANOVA for interaction (F(1, 46)) = 10.22 P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 Sidak’s post-hoc; pooled 2 independent experiments). e, Expression of IFN-γ receptor subunit mRNA by fluorescent in situ hybridization in slices from mouse PFC. RNA probes and corresponding colors: left:psd95-blue (neurons); right: CD11B-blue (microglia); top: IFNGR1-red; bottom:IFGR2-red. Yellow arrowheads denote co-localization. f, Expression of IFN-γ receptor subunit protein by flow cytometry. Cells were gated on Hoechst+/live/single then neurons and microglia were gated on NeuN and CD11B, respectively. Ifngr1−/− mice and no primary antibody for IFNGR2 were included as negative controls. g, Deleting Ifngr1 from neurons in the PFC caused social deficits. Ifngr1fl/fl mice were injected with AAV-Syn-CRE-GFP into the PFC and tested for social behavior 3 weeks post injection (n = 11;12 mice per group; ANOVA for genotype (F(1, 21)) = 10.62, P < 0.01; *P < 0.05 Sidak’s post-hoc; pooled 3 independent experiments). h, VgatCre::Stat1fl/fl mice exhibit social deficits (n = 10;11 mice per group; ANOVA for interaction (F(1, 19)) = 10.30 < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 Sidak’s post-hoc; pooled 3 independent experiments). i, Layer 2/3 neurons in slices from wild-type mice are held under tonic GABAergic inhibition (top), which is blocked by the GABA-A receptor antagonist bicuculline. IFN-γ increases tonic GABAergic inhibitory current (n = 11 cells from 4 mice; bottom). j, Holding current pre and during IFN-γ (P = 0.01 t-test). k, IFN-γ increased latency to reach each seizure stage (n = 6 mice per group; ANOVA with repeated measures < 0.001; ***P < 0.001 Sidak post-hoc) and (inset) reduced the maximum severity of seizures (***P < 0.001 t-test; repeated 2 times). l, Diazepam rescued social deficits in Ifng−/− mice (n = 12 mice per group; ANOVA for interaction (F(1, 22)) = 9.204 < 0.01; **P < 0.01 Sidak’s post-hoc; repeated 2 times). Data from the 3-chamber test (a, d, g, h, i) were analyzed by applying a 2-way ANOVA for social behavior and genotype/treatment, followed by a Sidak’s post-hoc test. Bars represent average mean times investigating ± s.e.m. All experiments were repeated at least once.