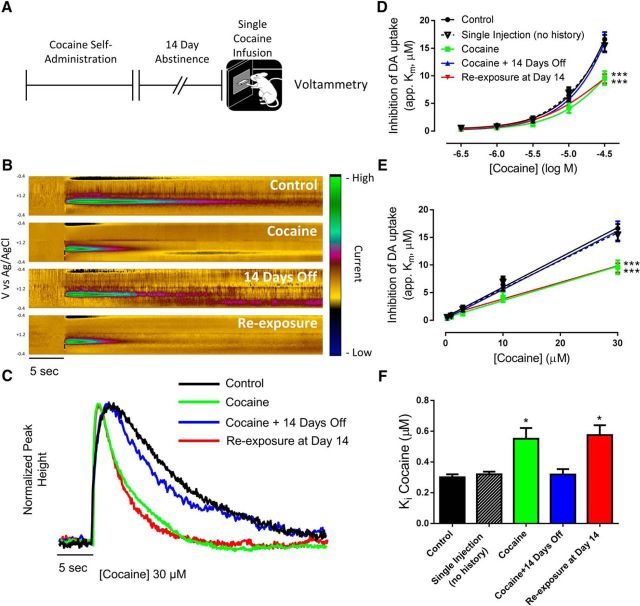
Figure 2.
Cocaine self-administration-induced cocaine tolerance in the NAc core is reinstated by a single cocaine injection. A, Experimental timeline. B, Dopamine (DA), as indicated by current (z-axis) occurring at its oxidation (+0.6 V) and reduction (−0.2 V) peaks (y-axis) across time (x-axis) is represented as pseudo-color plots following 30 μm cocaine. Representative color plots and traces (C) show that the ability of cocaine to slow dopamine uptake is blunted in rats with a history of cocaine self-administration, and after cocaine re-exposure. Logarithmic (D) and linear (E) concentration–response curves for cocaine show a downward shift in cocaine effects in the cocaine and re-exposure groups. F, Ki values for cocaine are increased in the cocaine and re-exposure groups, indicating decreased cocaine potency at the DAT. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 versus control. Control, n = 4; single injection, n = 4; cocaine, n = 5; cocaine + 14 days off, n = 5; re-exposure at Day 14, n = 8. Error bars indicate ± SEM.