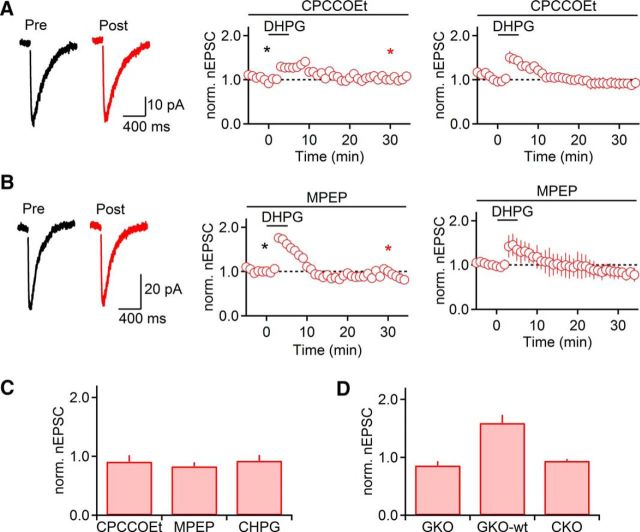
Figure 6.
Activation of both mGluR1 and mGluR5 is required for the induction of mGluR-nLTP. Recordings were performed with a Cs-based internal solution. A, DHPG failed to evoke mGluR-nLTP in the presence of the mGluR1 antagonist CPCCOEt (100 μm, n = 5). B, In the presence of the mGluR5 antagonist MPEP (50 μm), DHPG failed to evoke mGluR-nLTP (n = 5). A, B, Left, Representative traces recorded in control (black) and 30 min following DHPG application (red). A, B, Middle, Representative experiments show time course of nEPSC before and following DHPG application. Individual values indicate average over 5 consecutive time points. *Time points of recordings shown on left. A, B, Right, Summary data, expressed as mean ± SEM. C, Summary data quantifying the magnitude of mGluR-nLTP (measured at t = 26–30 min) in the presence of CPCCOEt (100 μm, n = 5) or MPEP (50 μm, n = 5) and following application of the mGluR5 agonist CHPG (500 μm, 5 min, n = 5) replacing DHPG. D, Summary data quantifying the magnitude of mGluR-nLTP (measured at t = 26–30 min) in slices derived from mGluR5 knock-out mice (GKO, n = 7), their WT littermates (GKO-wt, n = 4), and from GABAergic neuron specific mGluR5 knock-out mice (CKO, n = 3).