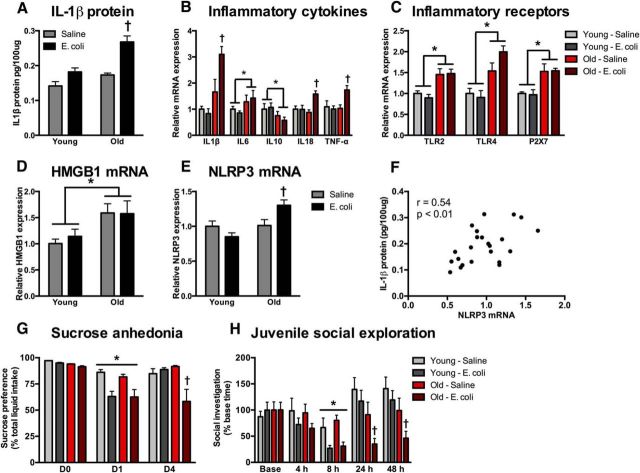
Figure 3.
Aged animals exhibit prolonged inflammation following infection. Hippocampal tissue was collected from young and aged rats 4 d following an E. coli or saline injection (n = 6/group). A–C, IL-1β protein and IL-1β gene-expression levels of inflammatory cytokines (B) and inflammatory receptors (C) were all evaluated. D–F, HMGB1 (D) and NLRP3 (E) mRNA expression were also evaluated and NLRP3 (F) was significantly associated with IL-1β protein. G, H, A separate cohort of rats (n = 8/group) underwent behavioral testing in a sucrose anhedonia (G) and juvenile social exploration task (H). Gene-expression data are presented relative to β actin. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. *, Main effect; †, simple effect of E. coli; in all cases p < 0.05.