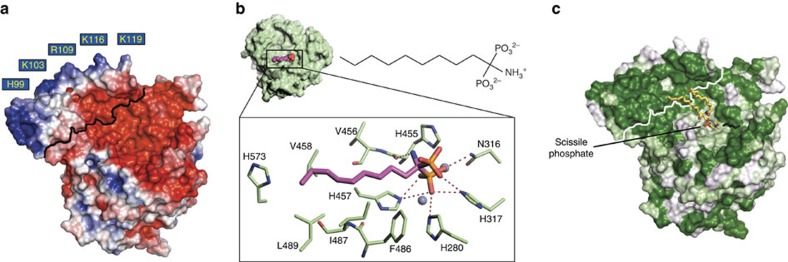
Figure 6. Electrostatic surface and substrate-binding site of ASMase.
(a) Electrostatic surface representation of open ASMase contoured at ±3 kT. The calculation was done at pH 7 to highlight relative charge differences, which are otherwise masked at pH 5. Positively charged residues proposed to interact with anionic membrane lipids are labelled. A black line demarcates the ASMasesap:ASMasecat boundary. A green outline marks the lipid-interacting surface on ASMasesap. (b) AbPA inhibitor bound to ASMase. Left: inhibitor shown as CPK spheres. Right: chemical structure of AbPA. Close-up, electrostatic interactions (red dashes) between AbPA (purple tail, orange and red phosphate) and zincs (spheres) and protein residues (green). (c) ASMase surface coloured by polar (white) to hydrophobic (dark green). A white line demarcates the ASMasesap:ASMasecat boundary. Sphingomyelin (yellow sticks) was docked manually into the active site. For comparison, the end of the AbPA lipid tail is shown as black sticks.