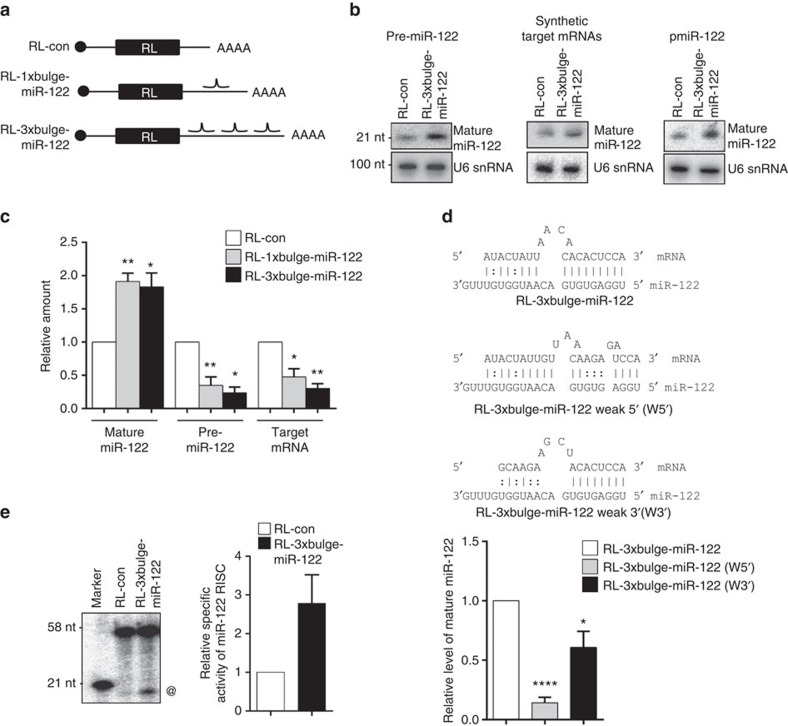
Figure 2. Target mRNA-dependent increase of mature miR-122 in human cells.
(a) Scheme of the different target mRNAs used. Positions of the miR-122-binding sites are indicated. (b) Effect of RL-3 × bulge-miR-122 on mature miR-122 level in cells transfected with pre-miR-122 and reporter plasmids or in vitro-transcribed mRNAs. In experiment described in the right panel, HEK293 cells co-transfected with plasmid encoding pre-miR-122 (pmiR-122) and RL reporters were used. Total RNA was extracted and northern blotted for mature miR-122, for all the experiments. U6 snRNA was used as loading control. (c) Mature miR-122, pre-miR-122 and target mRNA levels were quantified by quantitative reverse transcriptase–PCR in HEK293 cells expressing target mRNAs and co-transfected with plasmid encoding pre-miR-122. (d) Effect of modification of 5′ or 3′ miR-122-binding site on target mRNA-driven miRNA elevation. Relative quantification of mature miR-122 level increase in the presence of target RL-3 × bulge-miR-122 mRNA and in the presence of mRNAs with weak 5′- region (W5′) or weak 3′-region (W3′). Relative levels were normalized against respective target mRNA levels. (e) In vitro RISC cleavage assay done with protein equivalent amounts of affinity-purified FH-AGO2 isolated from pre-miR-122-transfected FH-AGO2 stable HEK293 cells expressing RL-3 × bulge-miR-122 or RL-con. @, Cleaved product of RISC assay; radio labeled 21-nt band serves as a marker. Paired two-tailed Student's t-tests were used for all comparisons. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001. Values plotted are means from at least three biological replicates for c and d, and two biological replicates for e. Error bars represent s.d.