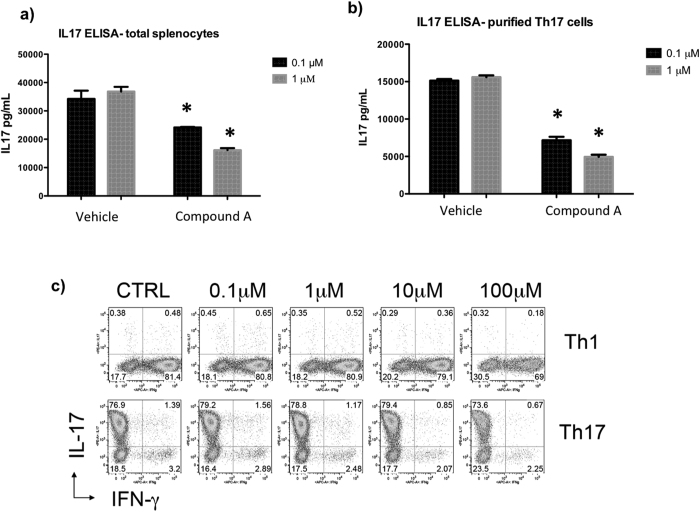
Figure 1. Inhibiting PI3Kδ results in potent, dose-dependent suppression of IL-17 production from total splenocytes and isolated Th17 cells.
(a) Transgenic OT II mouse total splenocytes, which contain T cells that are specific to ovalbumin peptide, were differentiated into Th17 cells and treated with inhibitor compounds at two different concentrations on day 3 of differentiation. Compared to vehicle control, the PI3Kδ inhibitor results in significant inhibition of IL-17 production in a dose-dependent manner as measured by ELISA (b) CD4+/CD62L+ naïve T helper cells were isolated from an IL-17F reporter mouse which uses Thy1.1 expression as a marker for IL-17F production, and then differentiated into Th17 cells. Th17 cells were then further purified by sorting thy1.1+ cells on flow cytometer and then treated with inhibitor compounds on day 3 of differentiation. Compared to vehicle control, the PI3Kδ inhibitor results in significant inhibition of IL-17 production in a dose-dependent manner as measured by ELISA. *p < 0.05, compared to DMSO (c) Transgenic OT II mouse total splenocytes, which contain T cells that are specific to ovalbumin peptide, were differentiated into Th1 and Th17 cells and treated with inhibitor compounds at two concentrations on day 1 of differentiation. Effects of the PI3Kδ inhibitor on T cell polarization were analyzed by intracellular staining by FACS.