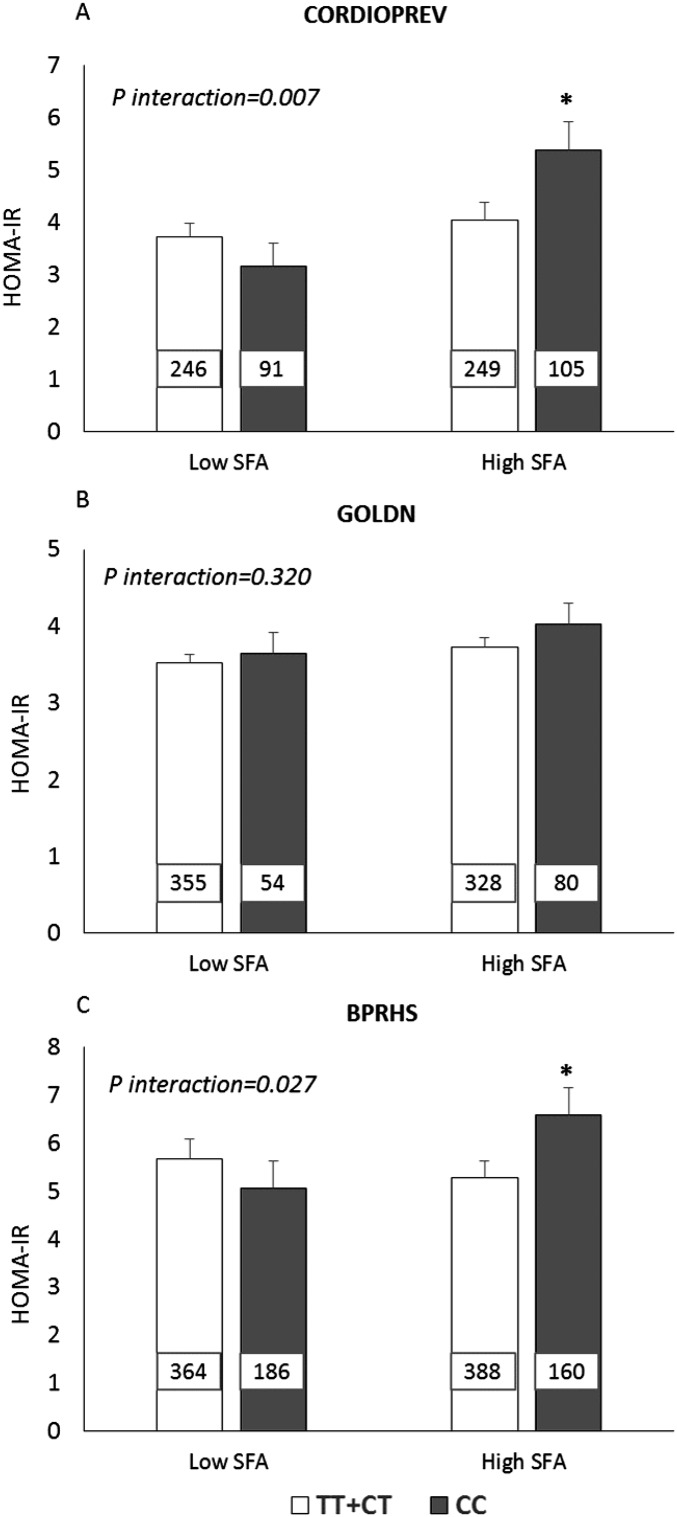
FIGURE 2.
Estimated mean ± SEM interactions between the S100A9 variant (rs3014866) and SFA intake (percentage of total energy) on HOMA-IR. (A) For the CORDIOPREV, low and high SFA intakes indicate median intakes (≤8.8% and >8.8%). (B) For the GOLDN, low and high SFA intakes indicate median intakes (≤11.8% and >11.8%). (C) In the BPRHS, low SFA and high SFA indicate SFA median intakes (≤9.3% and >9.3%). The number inside each bar indicates the number of subjects in that group with data available for HOMA-IR. Analyses were adjusted for age, sex, BMI, smoking status, alcohol use, diabetes medication use, and physical activity. In addition, we adjusted the model for the study center and family relationships in the GOLDN and for the population structure in the BPRHS. P-interactions between SFA intake (as dichotomous) and the S100A9 variant in each population were obtained with the use of a univariate model analysis. *P < 0.05 for mean comparisons of HOMA-IR values between CC and TT+CT genotypes with high SFA intake (univariate model analysis). BPRHS, Boston Puerto Rican Health Study; CORDIOPREV, Coronary Diet Intervention with Olive Oil and Cardiovascular Prevention; GOLDN, Genetics of Lipids Lowering Drugs and Diet Network; S100A9, S100 calcium-binding protein A9 gene.