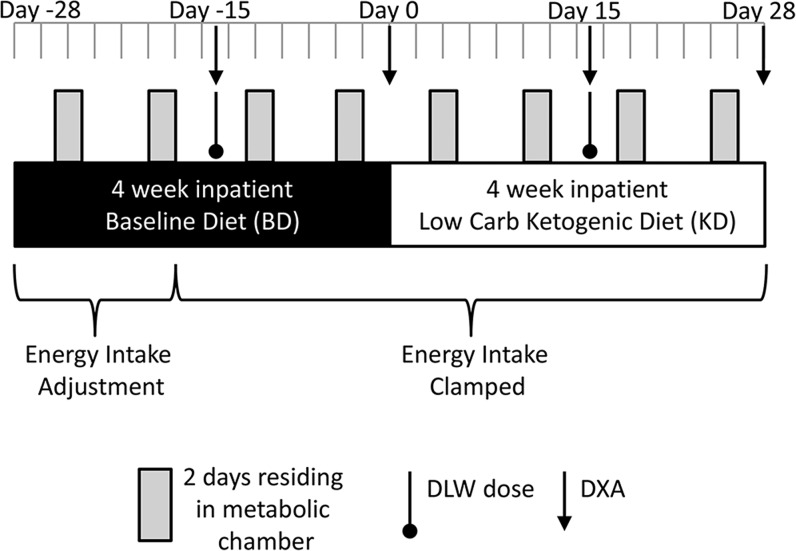
FIGURE 1.
Overview of the study design. Seventeen overweight and obese men were confined to metabolic wards where they consumed a BD designed to represent a habitual high-carbohydrate intake for a 28-d run-in period followed by an isocaloric KD for an additional 28 d. Dietary protein was kept constant throughout, and the subjects were prescribed 90 min of low-intensity daily aerobic exercise. Every week, subjects spent 2 consecutive days residing in metabolic chambers to measure total daily energy expenditure, respiratory quotient, and sleeping energy expenditure. Body composition was measured by DXA, and the average energy expenditure during the last 2 wk of each diet period was measured by the DLW method. BD, high-carbohydrate baseline diet; DLW, doubly labeled water; DXA, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry; KD, low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet.