Fig 3.
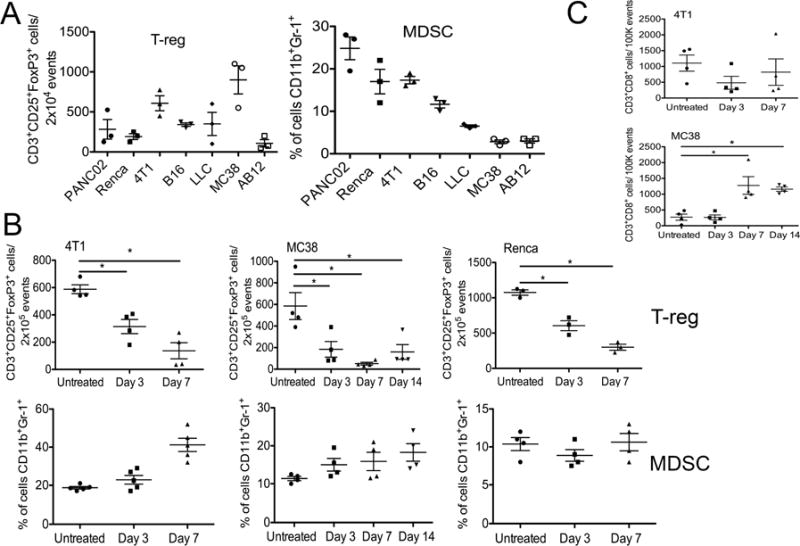
Resistance of different tumor models to oncolytic viral therapy is mediated by localized immune suppression within the tumor. (A) Baseline levels of regulatory T-cells (T-reg) and Monocyte Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSC) in tumors prior to therapy. Syngeneic subcutaneous tumors were formed from different cell lines and mice sacrificed when tumors reached 100 to 200 mm3 and disaggregated. Flow cytometry was used to quantify the relative levels of T-reg (CD3+CD25+FoxP3+CD8−) and MDSC (CD11b+Gr-1+) in the tumors. (B) Effect of viral therapy on suppressive immune cell profile within the tumor. Tumor-bearing mice were treated with a single low dose (1×107 PFU) intratumoral injection of WR.TK- and the levels of T-reg and MDSC in the tumors at different times after treatment were analyzed as in (A). (C) CD3+CD8+CD4− T-cells were also quantified in the tumor as in (A) (*p<0.05). Error bars ±SEM. See also Figure S3 and S4.
