Fig 5.
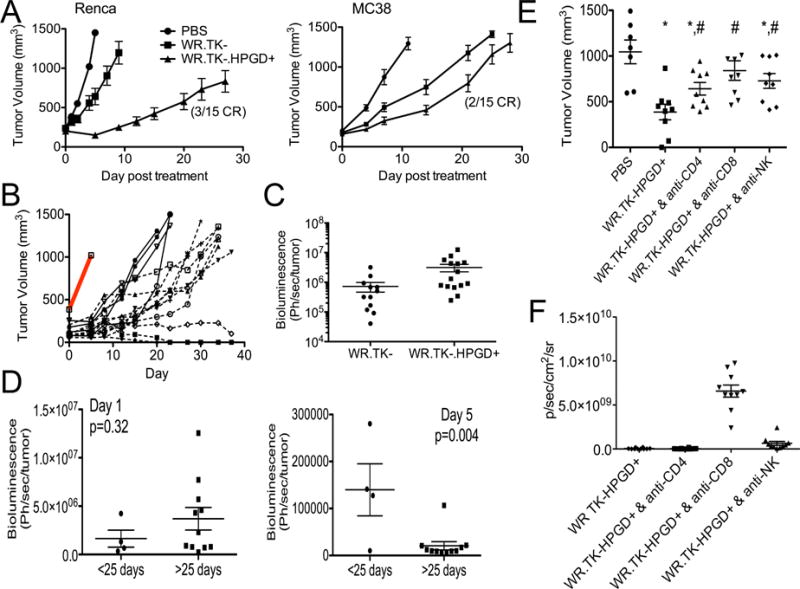
Enhanced therapeutic activity of WR.TK-.HPGD+. (A) Mice bearing subcutaneous RENCA or MC38 tumors were treated with a single intratumoral injection of PBS or 1×107 PFU of WR.TK- or WR.TK-HPGD+ and subsequent tumor growth followed by caliper measurement (n=15 per group). (B) Renca tumor growth in individual mice treated with WR.TK-HPGD+ are plotted, compared to PBS control (grey bar) and divided into good (solid line) and best (dashed line) responders. (C) The viral gene expression (bioluminescence) from the tumor at 24 hr after therapy was compared for mice treated with WR.TK- and WR.TK-HPGD+. (D) The bioluminescence signal (viral gene expression) from the tumor of mice treated with WR.TK-HPGD+ at day 1 and 5 were normalized to tumor volume and shown for both good and best responders. (E) The role of different immune subsets in the increased therapeutic activity of WR.TK-HPGD+ in Renca tumors was examined through depletion of CD4+, CD8+ and NK cells. (*p<0.05 v PBS; #p<0.05 v WR.TK-HPGD+). (F) Viral gene expression from the tumor (bioluminescence imaging) at day 3 after treatment of immune cell depleted mice. Error bars ±SEM. See also Figure S6
