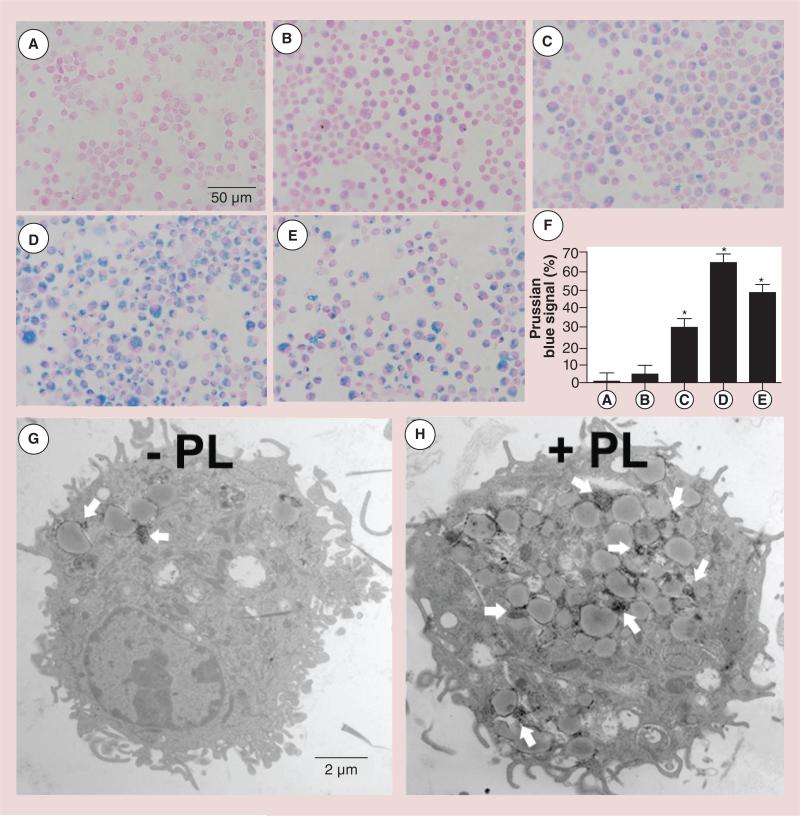
Figure 3. Prussian Blue staining to assess the effect of polylysine-induced internalization of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles by immature bone marrow dendritic cells that had been labeled for 12 h (Nuclear Fast Red counterstain).
(A) Nonlabeled bone marrow dendritic cells, (B) 500 μg/ml superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO), (C) 500 μg/ml SPIO plus 10 μg/ml PL mixture, (D) 500 μg/ml SPIO nanoparticles coated with PL during a 3-h preincubation and (E) 100 μg/ml SPIO plus 20 μg/ml PL mixture. (F) Quantitative analysis of the uptake of SPIO nanoparticles shown in (A–E) by MATLAB® (MathWorks, Inc., MA, USA). Data were expressed as means ± SE. (G & H) PL-mediated delivery of SPIO nanoparticles (white arrows) was confirmed by transmission electron microscopy.
*p < 0.05.
PL: Polylysine.
Reproduced with permission from [72].