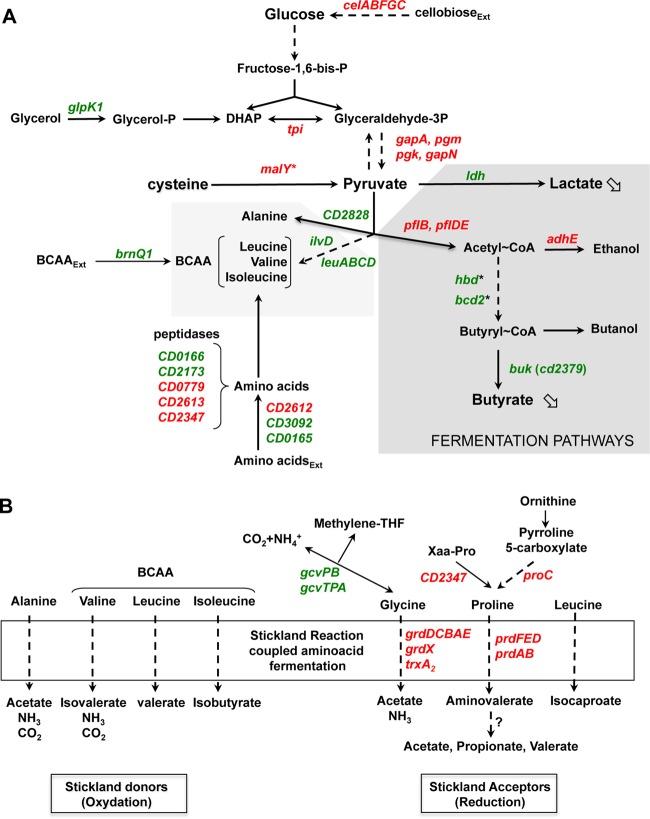
FIG 6.
Overview of C. difficile genes involved in carbon and amino acid metabolism that are differentially expressed in the presence of cysteine. Genes that are up- and downregulated in the presence of cysteine in the transcriptome analysis are indicated in red and green, respectively. An asterisk indicates that the differential transcript level was detected by qRT-PCR. (A) Carbon metabolism and fermentation pathways. Assignments of genes (listed with their products) regulated by cysteine availability are as follows: tpi, triosephosphate isomerase; gapA/gapN, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; pgk, phosphoglycerate kinase; pgm, 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate-mutase; celABC, PTS cellobiose; celF, cellobiose-6-P hydrolase; ldh, lactate dehydrogenase; adhE, aldehyde-alcohol dehydrogenase; pflB and pflD, pyruvate formate lyase; pflE and pflA, pyruvate formate lyase activating enzyme; thiA1, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase; bcd2, butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase; hbD2, 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase; crt2, 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydratase; buk, butyrate kinase; malY, cysteine desulfhydrase; ilvD, dihydroxy-acid dehydratase; leuA, 2-isopropylmalate synthase; leuB, 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase; leuC, 3-isopropylmalate dehydratase large subunit; leuD, 3-isopropylmalate dehydratase small subunit; brnQ1, BCAA transporter. (B) Stickland reactions and associated metabolism. Assignments of genes regulated in response to cysteine availability are as follows: grdDCBAEX, glycine reductase complex; prdEDBA, proline reductase; prdF, proline racemase; CD2347, putative Xaa-Pro dipeptidase; proC, pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase, gcvPB, glycine decarboxylase; gcvTPA, bifunctional glycine dehydrogenase/aminomethyl transferase protein.