FIG 6.
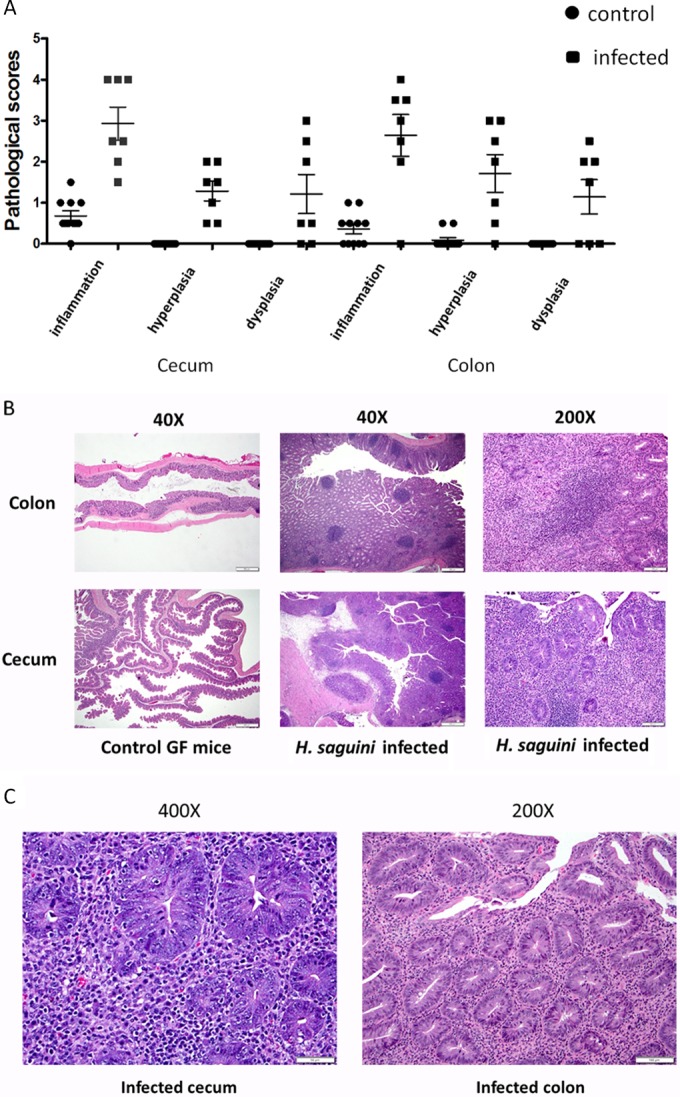
(A) H. saguini-infected monoassociated IL-10−/− mice had significantly higher inflammation, hyperplasia, and dysplasia scores than GF mice in both cecum and colon (P < 0.05). (B and C) H. saguini-induced typhlocolitis characterized by moderate to severe infiltration of inflammatory cells, including lymphocytes, histiocytes, and neutrophils, into the mucosa and submucosa, with epithelial defects, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) hyperplasia, and dysplasia (H&E staining).
