Figure 4.
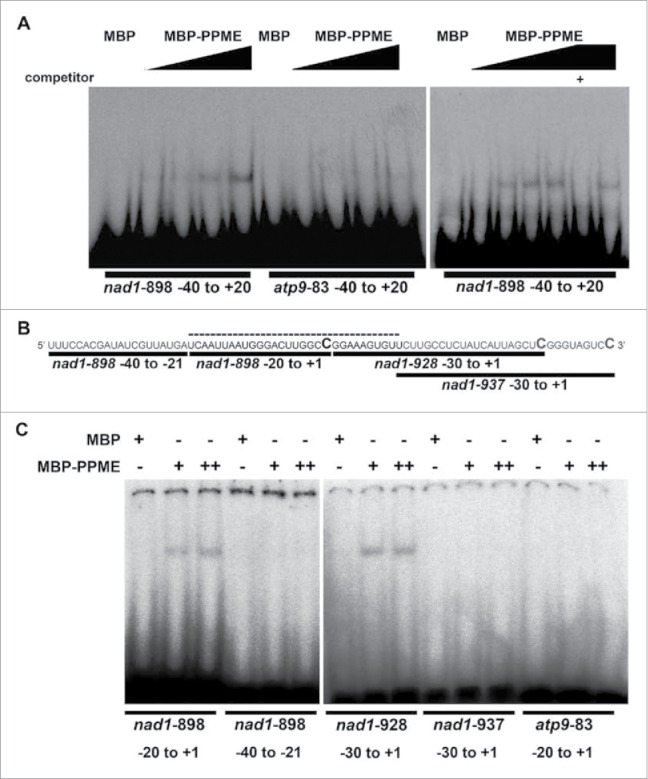
RNA-EMSA showing that recombinant PPME specifically binds to sequences surrounding the nad1-898 editing site. (A) MBP-tagged PPME recombinant proteins were co-incubated with nad1-898 probes or atp9-83 probes for sequences located up- and downstream of nad1-898 or atp9-83, respectively. The left panel shows the interaction between MBP-PPME and nad1-898 or atp9-83. The black triangles above each gel indicate the increasing concentrations of MBP-PPME in each gel. The right panel shows the binding between MBP-PPME and nad1-898, which was titrated by the exogenous addition of cold nad1-898 probe. +: cold competitor. (B) Nucleotide sequences of the probes specifically designed for EMSA. The RNA sequence (from 5′ to 3′) includes the region from the -40 nucleotide of nad1-898 to the +1 nucleotide of nad1-937. The bold C nucleotides indicate the corresponding nad1-898, nad1-928, and nad1-937 editing sites. The bold solid lines indicate the regions individually probed with specific probes, and the dotted line represents the putative nad1-898 cis-element recognized by PPME. 64. (C) RNA-EMSA revealed that among the 4 different probes, PPME specifically bound to only the nad1-898 −20 to +1 and nad1-928 -30 to +1 probes. However, the 20 nucleotides (putative cis-element for nad1-928) upstream of nad1-928 that overlapped with the nad1-937 −30 to +1 region did not exhibit PPME binding activity. The atp9-83 −20 to +1 probe was used as a cis-element negative control. The + and ++ symbols denote 200 nM MBP and 100 nM MBP-PPME or 200 nM MBP-PPME recombinant protein, respectively, and 200 pM probe was used for the all RNA-EMSAs.
