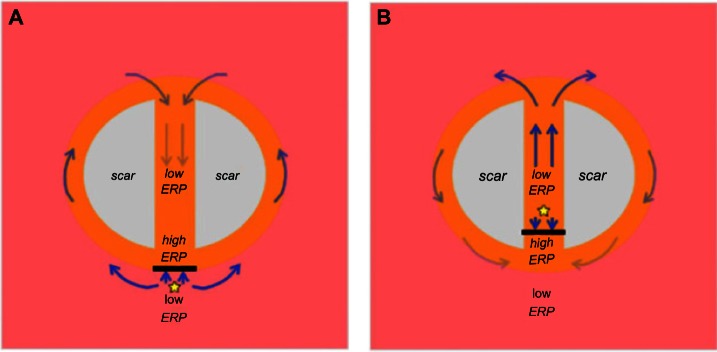
Figure 8.
Mechanism of arrhythmia induction following capture of a focal ectopic beat due to ERP gradients within the isthmus. (A) Focal ectopic occurs at the mouth of the isthmus, distal to the scar itself (ie, just outside main isthmus). Capture is blocked from directly entering the isthmus at the mouth due to the high ERP and is forced around the outer boundary of the scar where ERP is lower, entering the isthmus from the opposite side. In this time, tissue within the isthmus center has sufficiently recovered, and a reentrant circuit is established. (B) Focal ectopic occurs at the mouth of the isthmus, proximal to the scar itself (ie, just inside the isthmus). Capture is blocked from exiting the isthmus at the mouth due to the high ERP, but is allowed to propagate along the isthmus itself, exiting at the opposite end. Activation then proceeds to propagate around the scar boundary and reenters the isthmus, setting up a reentrant circuit.