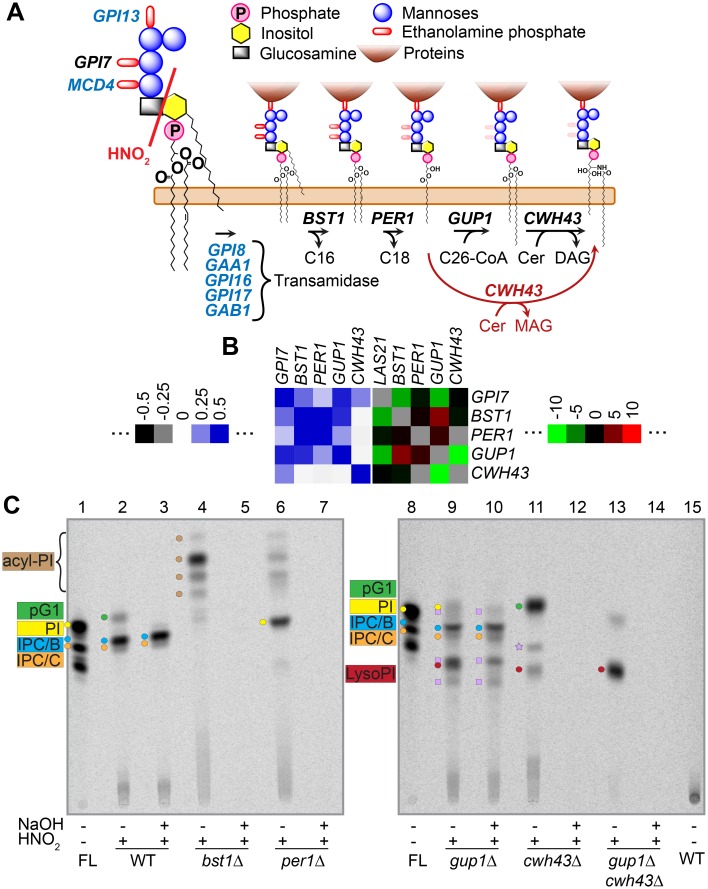
Fig 10. GPI anchor remodeling.
(A) the classical model of the lipid remodeling pathway for GPI proteins (black arrows) and a proposed additional route (red arrow)(adapted with permission from Fig 1 of [66]). Essential genes are indicated in blue. MAG = monoacylglycerol. Treatment with HNO2 selectively cleaves the glycosidic bond between GlcN and inositol. (B) correlations (left) and S scores (right) of the cluster of GPI anchor remodeling enzymes. Las21 (Gpi7) adds ethanolamine-phosphate to the second mannose (panel A) during GPI lipid biosynthesis and its deletion changes the structure of the GPI anchor. (C) free lipids (FL) and GPI anchor lipid moieties of WT and different remodeling mutants treated or not with nitrous acid (HNO2) and mild base (NaOH) as indicated. Lipids were separated on TLC using solvent 3. Light purple squares and stars indicate mild base resistant and mild base sensitive anchor lipids of unknown structure, respectively.