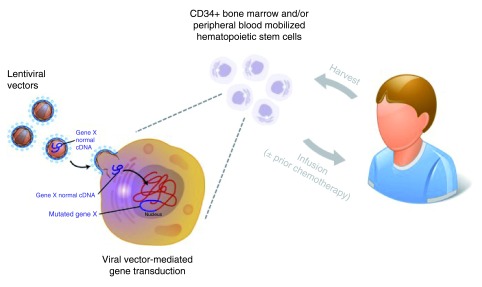
Figure 1. Schematic representation of a typical gene therapy procedure for primary immunodeficiency diseases (PIDs).
CD43+ hematopoietic progenitors are obtained through bone marrow harvest or peripheral blood apheresis after pharmacological mobilization. Cells are then cultured in vitro with cytokines and growth factors (e.g. SCF, TPO, and Flt-3 ligand) and exposed to viral vectors. Finally, transduced cells are collected and reinfused to the patient through a peripheral vein. If the gene therapy protocol involves myeloreductive chemotherapy, the cytoreductive agent is administered ~24 hours before the infusion of gene-corrected cells. (Graphics modified from original illustrations by Derryl Leja, NHGRI, Image Gallery, www.genome.gov).